- Newest
- Most viewed
Interested in a Link Placement?
Autonomous Joins NVIDIA Inception Program
Autonomous joins the NVIDIA Inception Program to accelerate AI innovation and product development.
Latest Updates | Apr 28, 2025 400 views

Liven App Review: A Mental Wellness Tool for Productivity and Focus
Work Wellness | Apr 28, 2025 702 views

Stool vs. Chair: Which is Better for Your Comfort and Productivity?
Smart Products | Apr 24, 2025 747 views

Understanding Standing Desk Prices: What to Expect at Every Budget
Smart Products | Apr 22, 2025 345 views
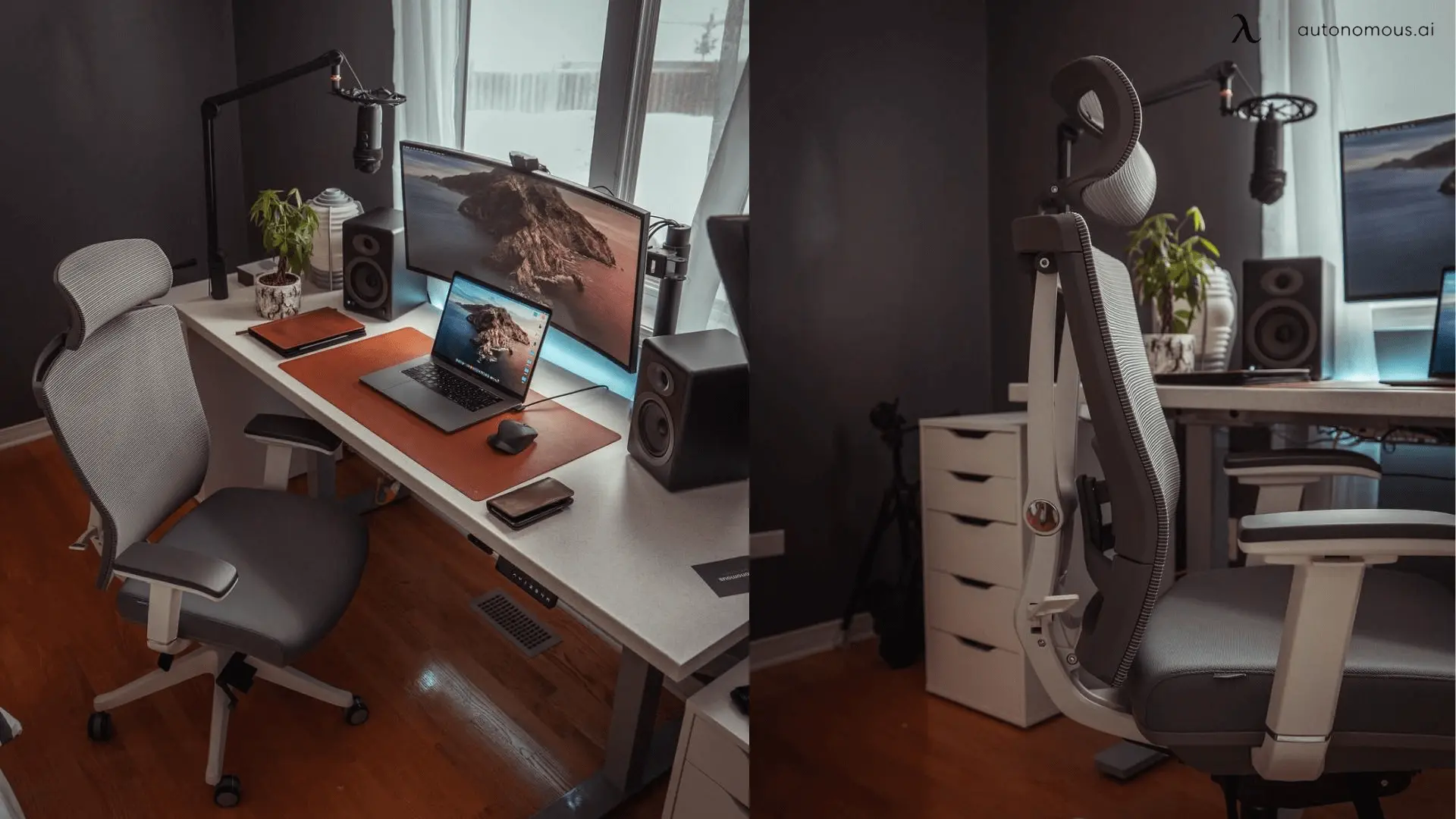

The 5 Best Office Chairs for Bedroom Setups in 2025
Smart Products | Apr 21, 2025 1,116 views
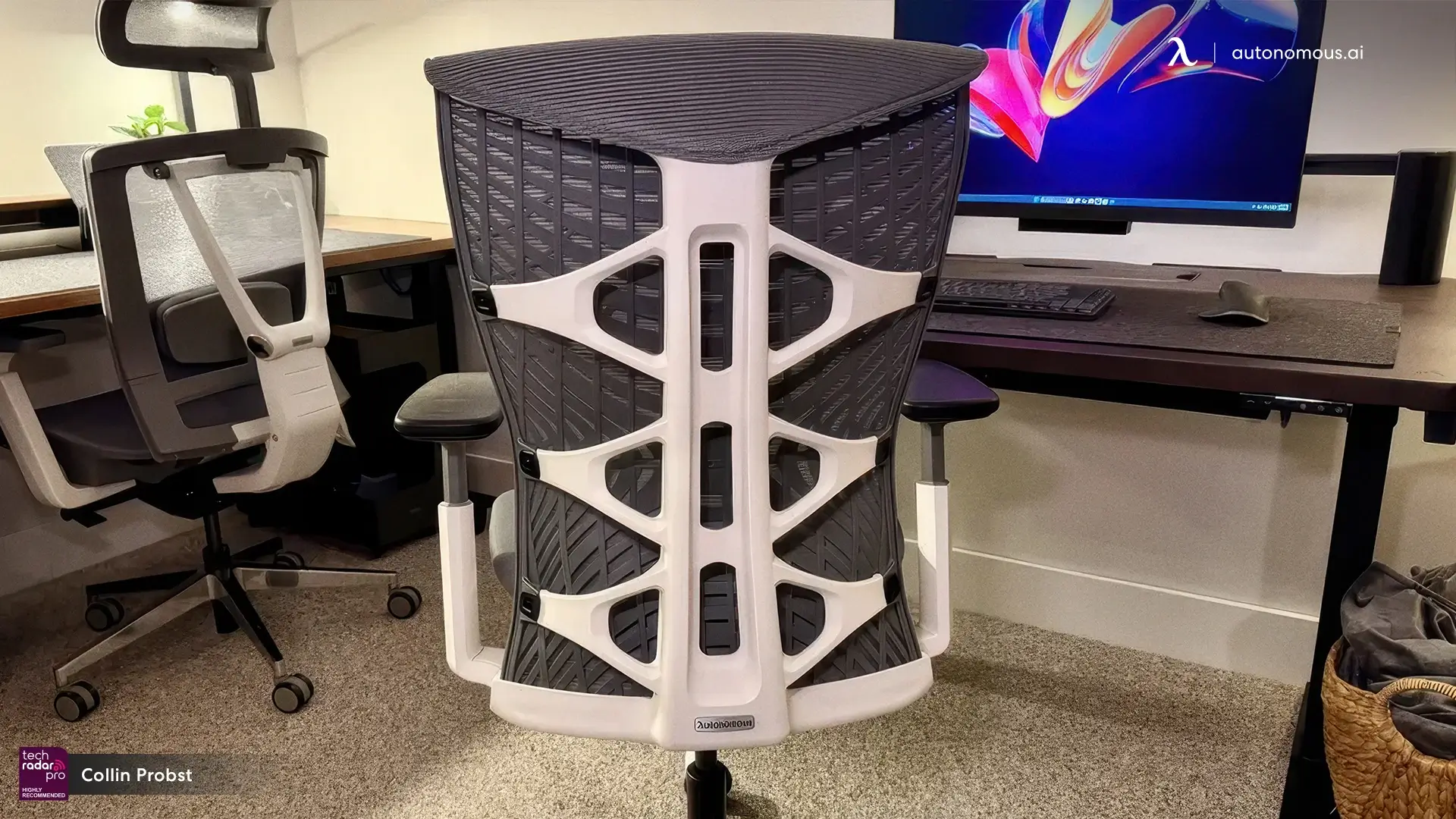

Best Office Chairs for Managers That Lead in Comfort and Support
Smart Products | Apr 18, 2025 1,211 views

Top 5 Adjustable Metal Standing Desks Worth Buying
Smart Products | Apr 17, 2025 818 views
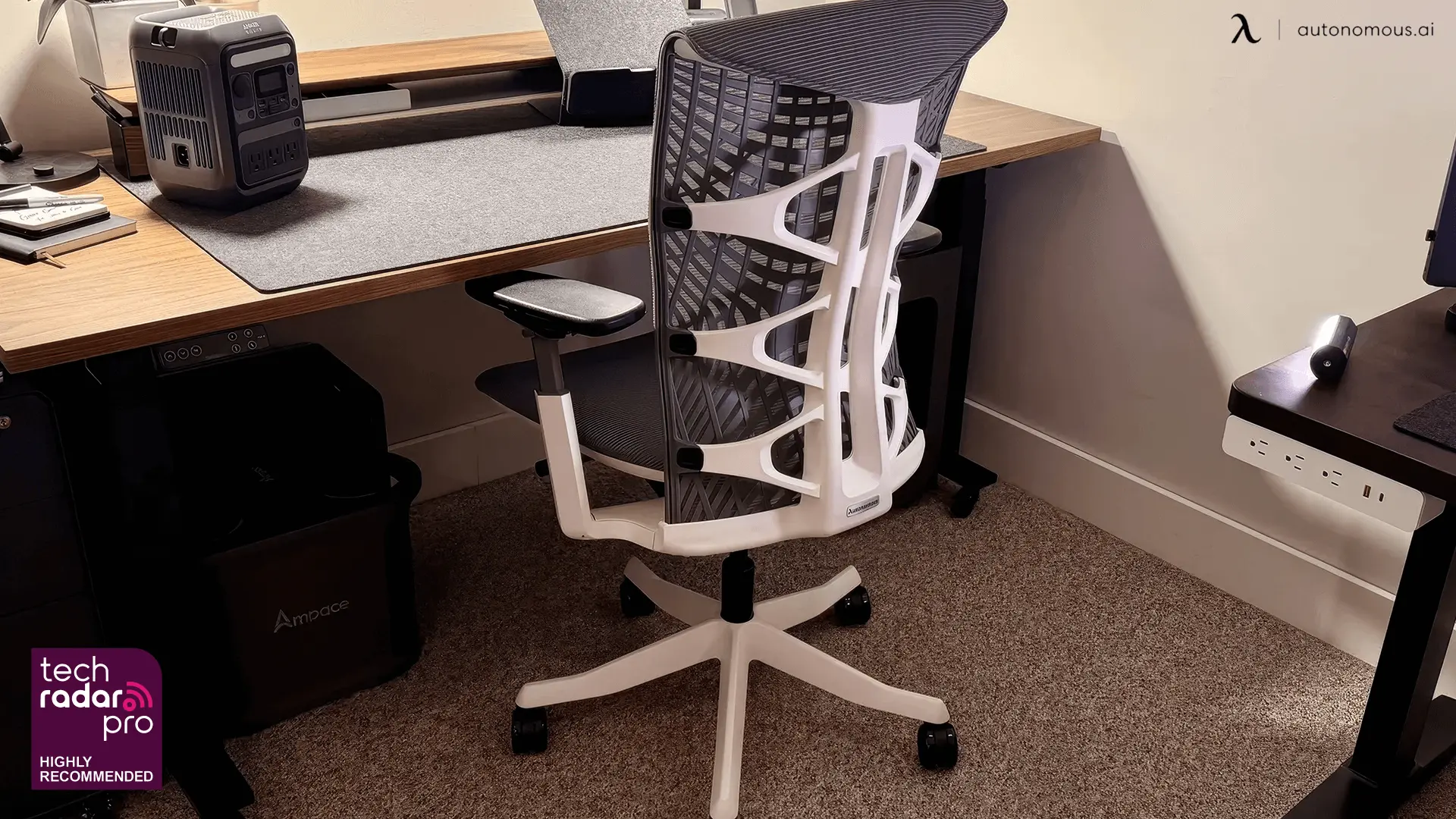

Best Office Chairs for Carpeted Floors: Comfort, Durability, and Style
Smart Products | Apr 16, 2025 1,178 views

10x10 Office Shed for Remote Workers: A Productive, Distraction-Free Space
Workplace Inspiration | Apr 15, 2025 911 views

Best Heavy Duty Standing Desks for Stability & Strength
Smart Products | Apr 14, 2025 1,269 views

ADU Zoning Explained: Everything You Need to Know
Workplace Inspiration | Mar 28, 2025 1,085 views

Vermont ADU Handbook: A Complete Guide to Building Your Own
Workplace Inspiration | Mar 28, 2025 1,234 views
.svg)
