ADUs in Georgia: Everything You Need to Know
Are you curious about building a special kind of small house in Georgia? These houses, called accessory dwelling units or ADUs, can be a great way to create extra living space on your property. In this easy-to-understand guide, we'll explore the rules and processes for building prefab ADUs in Georgia. ADUs offer a flexible housing solution, serving as additional accommodation for family, friends, or tenants.
Exciting options like prefab ADU builders and shed house ideas will also be discovered. They can also be used as a home office, art studio, or Airbnb rental. However, before embarking on your ADU project, it's crucial to familiarize yourself with the Georgia ADU rules and regulations, which vary by city or county. This article will serve as your comprehensive guide to building a prefab ADU in Georgia, covering everything from selecting a prefab ADU design to securing the necessary permits.
Cities and Counties Allowing ADUs in Georgia
Georgia is witnessing a growing trend of ADU acceptance in various cities and counties. However, it's important to note that regulations may differ significantly from one municipality to another. Here are some areas where ADUs are generally allowed:
- Atlanta
- Decatur
- Savannah
- Clarke County
- DeKalb County
- Fulton County
- Gwinnett County
- Cobb County
- Clayton County
- Henry County
Understanding the specific rules and regulations in your city or county is crucial when considering the construction of an ADU.
ADU Regulations in Georgia
ADU regulations in Georgia are designed to promote diversity and affordability and address the housing needs of the real estate market. Here is a summary of the regulations and requirements based on the provided information:
- Legalization and Zoning: ADUs were legalized in 2015 and are allowed in specific residential zoning districts, including R-85, R-60, R-50, RM-18, RM-22, and RM-43.
- Location and Placement: ADUs can be attached or detached from the main house and positioned behind existing houses or beside new constructions. If the ADU is not attached to the main house, it must be placed in the backyard and occupy at most 30% of the backyard's footprint.
- Size and Bedrooms: ADUs should be at most 40% of the main residence's floor space. The maximum size is 800 square feet, including the garage. Decatur ADUs have a limit of two bedrooms.
- Occupancy Verification: Owners must verify occupancy of either the main residence or the ADU.
- Lot Size and Impervious Surfaces: The combined square footage of the main house and ADUs cannot exceed 40% of the lot size. The impervious surfaces should be at most 40% of the lot's area.
Some cities and counties in Georgia may have different ADU regulations and requirements. It is advisable to research and consult with local authorities to obtain accurate and up-to-date information regarding ADU regulations in your desired location within Georgia.

Permitting Process for Prefab ADU in Georgia
You must obtain a building permit from the local planning and zoning department to build an ADU in Georgia. The permitting process may vary depending on the city or county where you plan to build your ADU, but here are some general steps and Georgia ADU laws to follow.
- Understand the regulations: Review the ADU rules for your zoning district and lot size. Ensure your ADU design meets the location, size, bedrooms, and impervious surfaces standards.
- Prepare a site plan: Create a plan showing the ADU's dimensions, location, setbacks, parking, utilities, and landscaping.
- Submit your plan: Take your site plan and ADU design to the planning and zoning department for review. Pay the fee and include additional documents like floor plans and engineering drawings.
- Obtain the building permit: Once your plan is approved, apply for the building permit. Pay the fee and provide the necessary information, such as insurance and contractor license.
- Begin construction: With the permit in hand, start building your ADU—schedule inspections to ensure compliance with building codes and regulations.
- Obtain the certificate of occupancy: Once construction is complete, get a certificate of occupancy from the building department. This certifies that your ADU is safe for use.
Variations in ADU Regulations in Georgia
ADUs (Accessory Dwelling Units) are generally permitted in most residential zoning districts in Georgia, but it's important to be aware of potential variations in regulations and requirements across different cities and counties. Here are a few examples:
- Savannah: Savannah is currently reviewing its zoning standards for ADUs to address housing needs. Current requirements include having a bathroom, kitchen, and bedroom and meeting setback and height regulations. Design review is also necessary for neighborhood compatibility.
- Decatur: ADUs are allowed in most residential zones in Decatur. However, the owner must reside in either the main dwelling or the ADU for at least eight months per year. The floor area of ADUs is limited to 800 square feet or 40% of the primary dwelling, with a maximum of 1,000 square feet if combined with a garage.
- Atlanta: ADUs in Atlanta can be accessory dwellings on the same lot, with a maximum size of 750 square feet. They must have a separate entrance from the main dwelling and should be architecturally compatible with the main dwelling. Short-term rentals are not permitted.
These examples demonstrate the variations in ADU regulations in Georgia. It's crucial to consult your local planning and zoning department for specific guidelines in your area. By following the local regulations, you can ensure the legality and safety of your ADU.

Tiny House Regulations in Georgia
Tiny houses offer an affordable and minimalist lifestyle, but it's important to understand the regulations governing them in Georgia. Compliance with tiny house laws in Georgia depends on your tiny house's type, size, and location. Here are the basic rules according to the types:
- RVs: These are temporary or seasonal motorized or towable vehicles. They must meet the ANSI A119.2 Standard but may have restrictions on parking and usage locations.
- Manufactured homes: These factory-built homes are transported on a chassis and meet HUD standards. They have limitations on placement and usage.
- Modular homes: Factory-built homes transported in sections and assembled on a foundation. They adhere to the International Residential Code (IRC) and Georgia State Minimum Standard Codes, subject to building and zoning regulations.
- Site-built homes: Homes constructed on-site on a permanent foundation, following the IRC and Georgia State Minimum Standard Codes, subject to building and zoning regulations.

Properties That Qualify
ADUs in Georgia are typically eligible for the following types of properties:
- Single-Family Properties: Many single-family homes in Georgia qualify for ADUs, making them a popular choice among homeowners looking to expand their living space or generate additional income.
- Duplex and Multifamily Properties: Regulations for ADUs in these property types may differ, and it's important to review local guidelines for eligibility and design specifications.
Property Designations
Local regulations may designate ADUs by various names, such as "granny flats," "in-law suites," or simply "accessory dwelling units". Understanding these designations in your area is essential, as they may come with specific rules and requirements.

Development Standards
Development standards for ADUs in Georgia encompass several crucial aspects, including:
Size Restrictions
Local rules in Georgia cities and counties set ADU size limits:
- ADUs plus the main house can't exceed 800 sq. ft.
- Up to 1,000 sq. ft. is allowed for ADU and garage.
- Some places permit two bedrooms in an ADU.
ADU rules like height, design, parking, and more vary by location. Check local restrictions and zoning before starting your project. Visit your local government or planning agency's website for info or reach out for help.
Example: In Decatur, ADUs can be 800 sq. ft. max and no more than 40% of the main house. If behind, the rear setback might be 5 feet.
In Atlanta, ADU size depends on zoning and overlay districts. In R-4 and R-5 areas without overlays, detached ADUs can't exceed 20 feet in height. With a Beltline overlay (BL) in R-4 and R-5 zones, 25 feet is the maximum height.

Setback Requirements
The setback requirements for ADUs in Georgia vary depending on the location of the property and the type of ADU. In general, most jurisdictions in Georgia require a minimum of 4 feet for the side and rear yard setbacks for ADUs. However, some also have specific setback requirements for the front yard, the street side yard, or the accessory structures.
It is important to check the specific regulations and zoning codes of your city or county before you start your ADU project. You can find the relevant information on the official websites of your local government or planning department. You can also contact them directly to ask questions or request assistance.
Fire Safety Measures
Fire safety is important for every home, including accessory dwelling units (ADUs). Here are some fire safety measures for ADUs in Georgia:
- Install smoke detectors and carbon monoxide detectors on every level of the ADU, including the basement and attic. Test the detectors monthly and replace the batteries every year.
- Have a working fire extinguisher in the kitchen and near any other potential fire hazards.
- Create a fire escape plan and practice it regularly with all household members. The plan should include two ways to escape from each room and a meeting place outside the ADU.
- Keep all flammable materials away from heat sources. This includes items such as gasoline, paint, and cleaning supplies.
- Make sure all electrical wiring is up to code and that all electrical appliances are in good condition.
- Have your chimney cleaned and inspected by a qualified professional every year.
- Clean the lint trap in the dryer after every use.
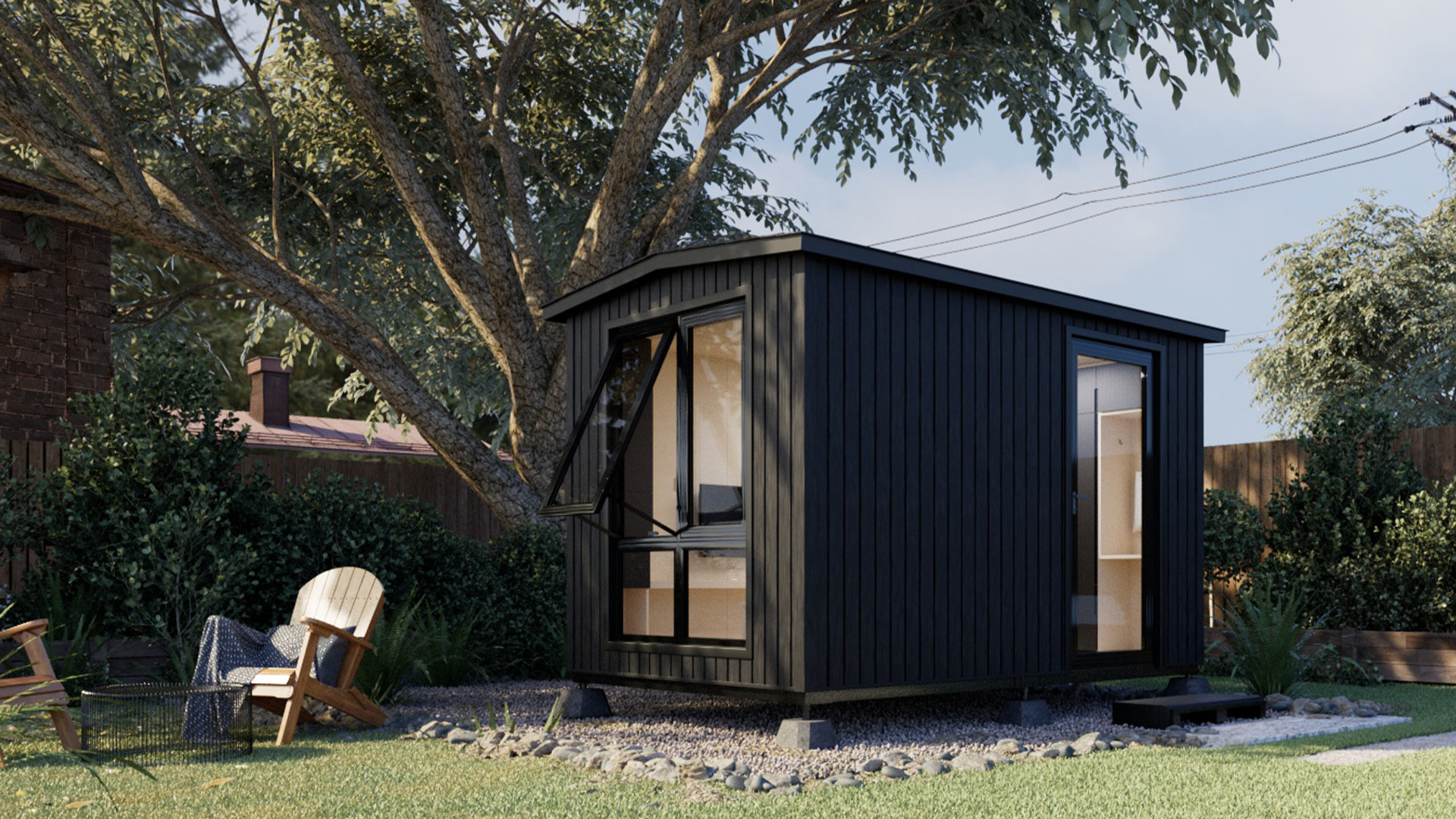

Height Restrictions and Limitations
The height of ADUs in Georgia varies by city or county. Most jurisdictions have a 16-foot height limit, but some may allow up to 20 feet if the ADU is combined with the garage. ADUs can have up to two stories.
Always check the specific regulations and zoning codes of your city or county before starting your ADU project. You can find the relevant information on the official websites of your local government or planning department.
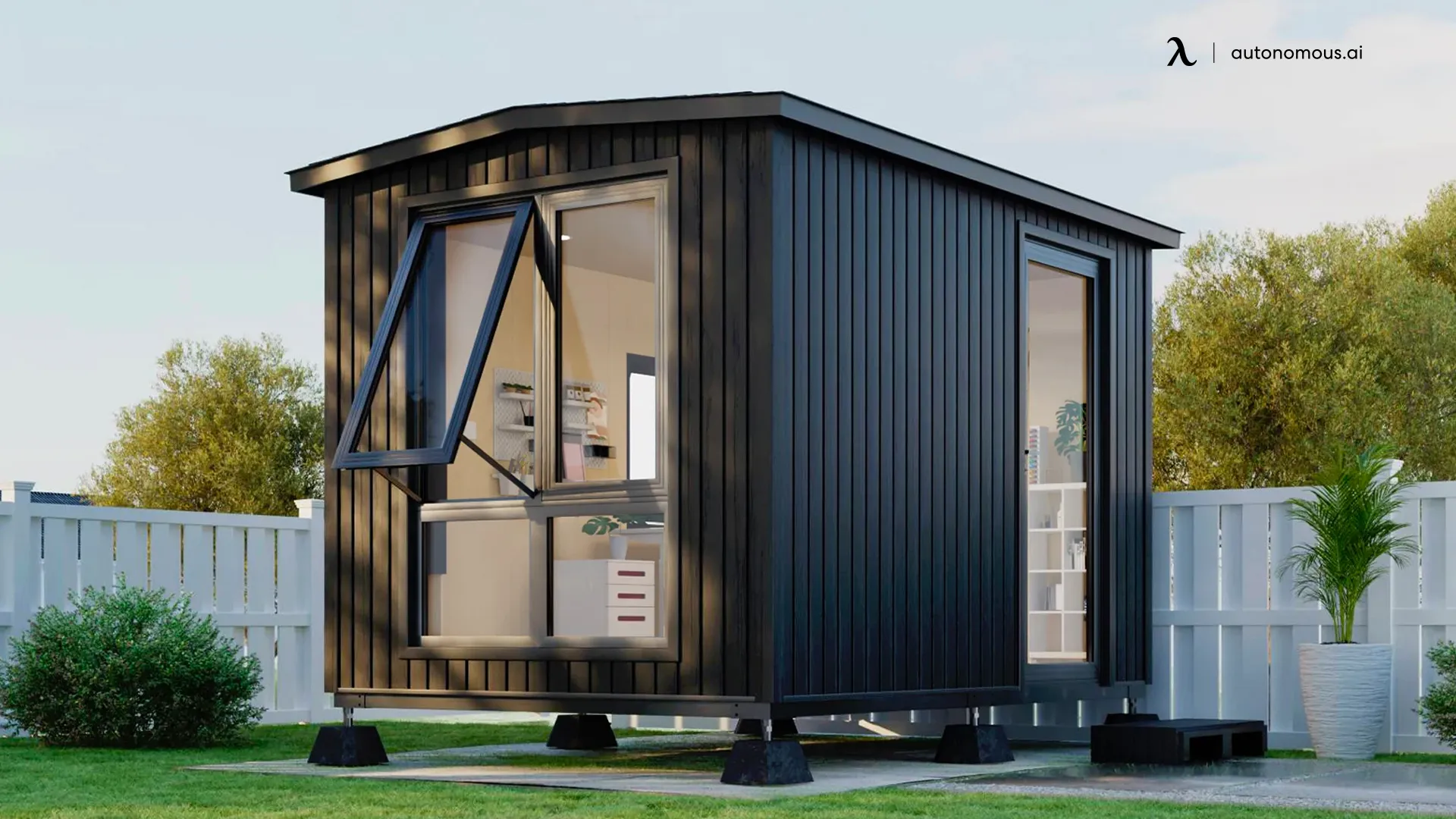
Autonomous ADUs: Modern, Convenient, and Sustainable Living in Georgia
Looking for a contemporary and hassle-free way to build an ADU in Georgia? Consider Autonomous ADUs, smart pods that offer self-reliant living. Here's what makes them appealing:
- Smart Features: These pods have sensors and smart devices to regulate temperature, lighting, security, and more.
- Adaptability: The space can be tailored to your needs with modular furniture and appliances.
- Voice Assistance: Interact with built-in voice assistants for convenience.
For top-notch Autonomous ADUs, visit Autonomous.ai. Their pod ADUs serve as home offices, studios, guest houses, or rental units. Choose from various sizes and designs to fit your requirements and budget. Order online, and they'll deliver and install it within weeks.

FAQs
1. What is ADU real estate?
ADU real estate has an accessory dwelling unit (ADU), a secondary housing unit on the same lot as the main dwelling. ADU real estate lets homeowners create extra living space for rental income, multigenerational or caregiver housing.
2. What are ADU appliances?
ADU appliances are electrical and mechanical devices in accessory dwelling units. They include refrigerators, stoves, washers, dryers, and HVAC systems. They make the ADU comfortable and convenient for living.
3. Can I rent out my ADU in Georgia?
Yes, in many Georgia cities and counties, you can rent out your ADU to tenants. However, checking with your local regulations and zoning ordinances is important to ensure compliance with any specific requirements or limitations on rental properties in your area.
4. What are ADU height restrictions in Georgia, and why do they matter?
ADU height restrictions in Georgia refer to the maximum allowable height for Accessory Dwelling Units. These restrictions are in place to ensure that ADUs do not disrupt the aesthetics of neighborhoods, block sunlight, or obstruct views. It's essential to understand these restrictions to comply with local regulations and maintain the character of your community.
5. Are ADU height restrictions the same across all cities and counties in Georgia?
No, ADU height restrictions can vary from one city or county to another in Georgia. Each municipality has its own zoning and building codes, which may include specific height limitations for ADUs. To ensure compliance, it's crucial to check with your local zoning and planning department or consult with ADU builders in Georgia who are familiar with the regulations in your area.
6. How can I determine the ADU height restrictions for my specific location in Georgia?
To determine the ADU height restrictions in your area of Georgia, contact your local zoning and planning department. They can provide you with information on the maximum allowable height for ADUs, setback requirements, and other regulations specific to your jurisdiction. ADU builders in Georgia can also help you navigate these restrictions while planning and constructing your ADU.

Conclusion
A growing number of Georgians are opting for ADUs because of the variety of advantages they provide. However, it is important to research the local ADU norms and regulations in Georgia before beginning your project.
ADUs in Georgia offer homeowners a chance to improve their properties and meet housing needs differently. By exploring ADU real estate options, considering the necessary appliances, learning about granny pods, or choosing a small log cabin, individuals can find suitable and attractive solutions for their housing needs. Georgia’s ADU regulations and the flexibility they allow enable creative and functional living spaces that add to a diverse and dynamic housing market.
This page has offered a thorough introduction to ADUs in Georgia, including topics such as who is eligible, what the design requirements are, where they may be built, and how tall they can be. Get in touch with Georgia ADU builders to discuss your choices and get the ball rolling on your ADU construction project if you're thinking about constructing one in the Peach State. Get your ADU now and enjoy the experience.
Spread the word
.svg)


.webp)
.webp)