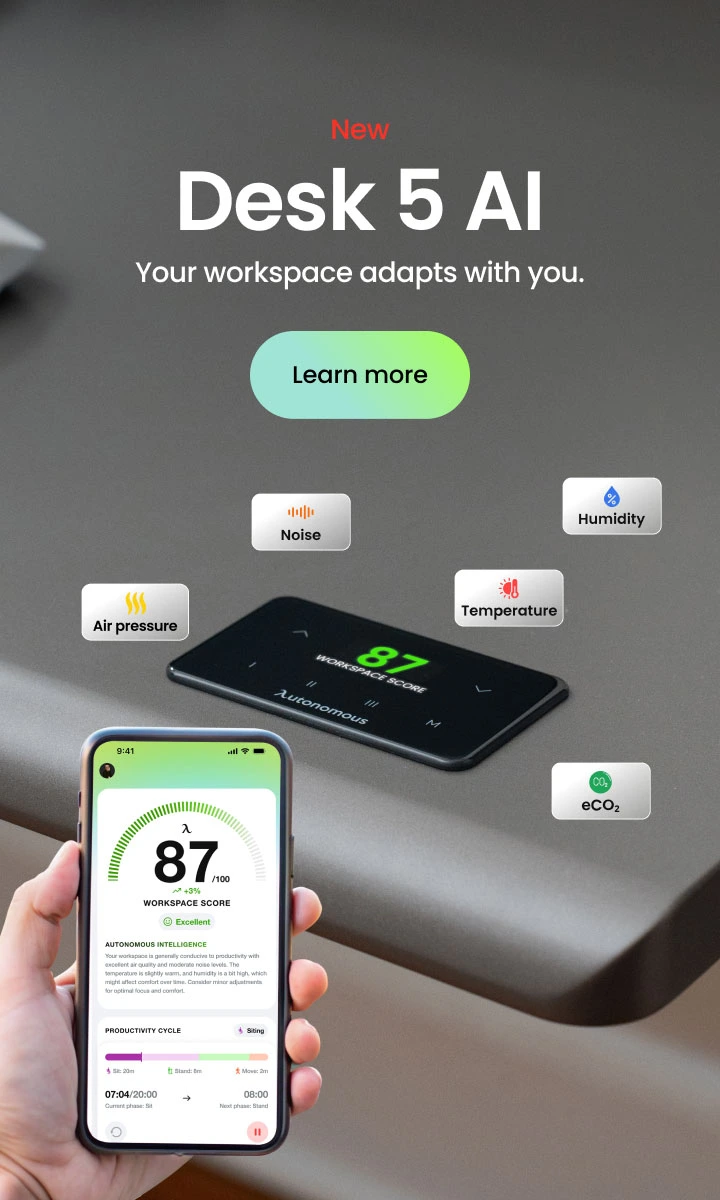
What Is a Tiny House Zone? All You Need to Know
Many people are falling in love with the idea of living in a tiny house, and we don't blame them! They have everything you need in a small space that's much easier to clean, maintain, and transport. However, living in a tiny house isn't as easy as it sounds, and it is because we have something called zoning regulations, which dictate whether we can permanently live in one of these houses or not. Today, we will provide a comprehensive guide on tiny house zones and all the essential information you need before purchasing one. We will go through tiny house zoning laws, and all the different approaches and examples of tiny house zoning, so keep reading!
What Is Tiny House Zoning? Building Codes Versus Zoning
The first thing you must know is that tiny house zoning regulations focus on how you use your land, as sometimes you can only build certain types of houses in a determined terrain. Zoning laws explain which structures are allowed in certain zones. They can specify minimum lot sizes, setback requirements, height restrictions, and other parameters that impact the placement and size of structures, including tiny houses.
However, building codes establish safety and construction standards that must be followed during the building process. They cover various aspects of construction, including structural integrity, electrical systems, plumbing, fire safety, and more. Building codes are intended to ensure that buildings are safe, habitable, and meet the minimum standards for people to live in them.
If you're going to build a tiny house, you must always check your tiny house zoning regulations. This is because certain jurisdictions don't specify what to do about tiny houses and may force you to stick to the same requirements as regular houses. This can create legal challenges if you want to live in a tiny house.
Nonetheless, if you live in certain jurisdictions that promote the use of tiny houses, you might be in luck. These states created separate categories of definitions for tiny houses, establishing minimum size thresholds and providing guidelines for parking, utilities, and other considerations. However, in many areas, the current zoning codes don't explicitly address tiny houses, making it difficult for people to build and live in their dream tiny houses.
If you're interested in tiny houses and want to navigate these complexities, you must research and understand the specific tiny house zoning regulations in your desired location. This includes consulting with local planning departments, zoning officials, or legal professionals to determine if tiny houses are allowed in your state and if any additional permits or variances are required to comply with the regulations.
Another thing to keep in mind is that no matter the size of your house, you will still have to comply with your state's building codes. These codes help ensure the structural integrity and safety of the dwelling, regardless of its size.
In summary, tiny house zoning refers to the regulations set by local governments that govern the placement and use of tiny houses. Zoning laws primarily focus on land use and dictate where and how tiny houses can be located. Nonetheless, building codes establish construction and safety standards that must be met during the building process. Both sets of regulations play a crucial role in determining the feasibility and legality of tiny houses in a specific area.
Types of Tiny Homes
1. Tiny Houses on Wheels (THOWs)
These houses are one of the most popular tiny houses out there because they are built on a trailer chassis, so people can even travel in them and never leave their homes. THOWs are popular for their mobility and flexibility, allowing homeowners to travel or change locations as desired.
2. Small Houses or Cottage-style Tiny Homes
If you prefer something that looks like the tiny version of a traditional house, this is the one for you. They have a fixed location and are not intended for mobility. Small houses often feature a loft area for sleeping to maximize space, and they may have multiple levels or separate rooms to provide a sense of privacy.
3. Container Homes
By repurposing containers, these homes offer a unique and sustainable housing solution. Moreover, you can customize your container home to include multiple containers or combine them with other materials to create larger living spaces.
4. Tiny Apartments
Many people are familiar with these compact living spaces located within larger multi-unit buildings. You don't have to worry too much about finding a good tiny apartment, as they're virtually everywhere and are the perfect solution for college students or young couples who want a place for themselves.
5. Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs)
ADUs are our favorite option when it comes to tiny houses. They are small secondary dwellings usually placed on the same property as a primary residence. Modular ADUs can be detached or attached to the main house and are often used as guesthouses, rental units, or housing for family members. You can customize your ADU to fit different architectural styles and include all the utilities and amenities you'd like.
6. Yurts and Tents
These non-permanent structures can be used as tiny homes or temporary living spaces. Yurts are circular, semi-permanent structures with a lattice frame and fabric covering. They are durable, energy-efficient, and offer a unique living experience. Tents, on the other hand, provide a more temporary and portable option for minimalist living or outdoor adventures.
7. Floating Homes
These tiny homes are designed to float on water, often found in marinas or residential communities near lakes, rivers, or coastlines, so they're the best option if you live near a body of water. Floating homes are built on floating platforms or pontoons and provide a unique and alternative living experience surrounded by water.
States with Flexible Building Codes or Zoning Regulations
Although building codes and tiny house zone regulations can vary significantly between states and even within specific regions, several states are known for having relatively flexible building codes or zoning regulations that can be more suitable for alternative housing options, such as tiny homes. Here are a few examples:
1. California
California has been at the forefront of embracing alternative housing options. In 2016, the state adopted legislation allowing Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) statewide, making it easier for homeowners to build smaller dwellings on their properties. Modular homes in California are widely accepted, so you can go ahead and get the house you've always wanted!
2. Oregon
Oregon has made it easier for individuals to build and live in tiny homes. The state has adopted flexible tiny house zones that recognize tiny houses as dwelling units and has regulations that allow them to be used as primary residences. Several cities within Oregon, such as Portland, have embraced tiny homes and have specific zoning regulations for building them.
3. Texas
Texas is known for having fewer zoning restrictions and more lenient building codes in certain areas. The truth is that Texas can be a pretty tricky state regarding tiny housing regulations because you will have to adapt your home depending on which jurisdiction you live in. Some cities, such as Austin and Houston, have been more open to alternative housing options and have great regulations for those who want to build tiny houses.
4. Colorado
Colorado has seen a rise in interest in tiny homes, and some municipalities have responded by adopting more flexible regulations. However, if you want to play safe, your best option is to get an ADU or a tiny home on wheels, as those are the most widely accepted tiny houses in Colorado. Denver, for example, has implemented tiny house zone changes to allow for ADUs and has established guidelines specifically for tiny homes.
5. Florida
Florida is known for having less stringent building codes and tiny house zone regulations compared to some other states. This can make building prefab accessory dwelling units in Florida much more accessible, especially in areas that are more rural or less densely populated. However, specific regulations vary by county and municipality, so you must still research your local requirements.
It's worth noting that although these states have flexible regulations, there can still be variations and specific requirements within each jurisdiction. Therefore, researching and consulting with the local authorities, planning departments, or legal professionals is crucial to understand the regulations in your specific location before pursuing any construction or housing plans. This is important for building prefab homes in Southern California, a prefab ADU in San Diego, or many other places.
ADUs Allowed in All States
If, after reading all of this, you're still worried about whether you'll be able to build a tiny house in your backyard or not, we want to show you our three most popular options for tiny housing, which are allowed all across the country. This will lift a weight off your shoulders and let you have the tiny house of your dreams.
1. Autonomous WorkPod Versatile
The Studio Pod boasts a sleek and modern design that can complement various interior aesthetics. Its compact size makes it ideal for small spaces, apartments, or home offices, where it is crucial to make the most of our space.
One of the most practical features of this prebuilt studio is its soundproofing capabilities. It is equipped with acoustic panels that effectively reduce external noise, allowing for a quieter and more conducive work environment. The pod also features integrated ventilation to maintain airflow and prevent stuffiness during extended work sessions.
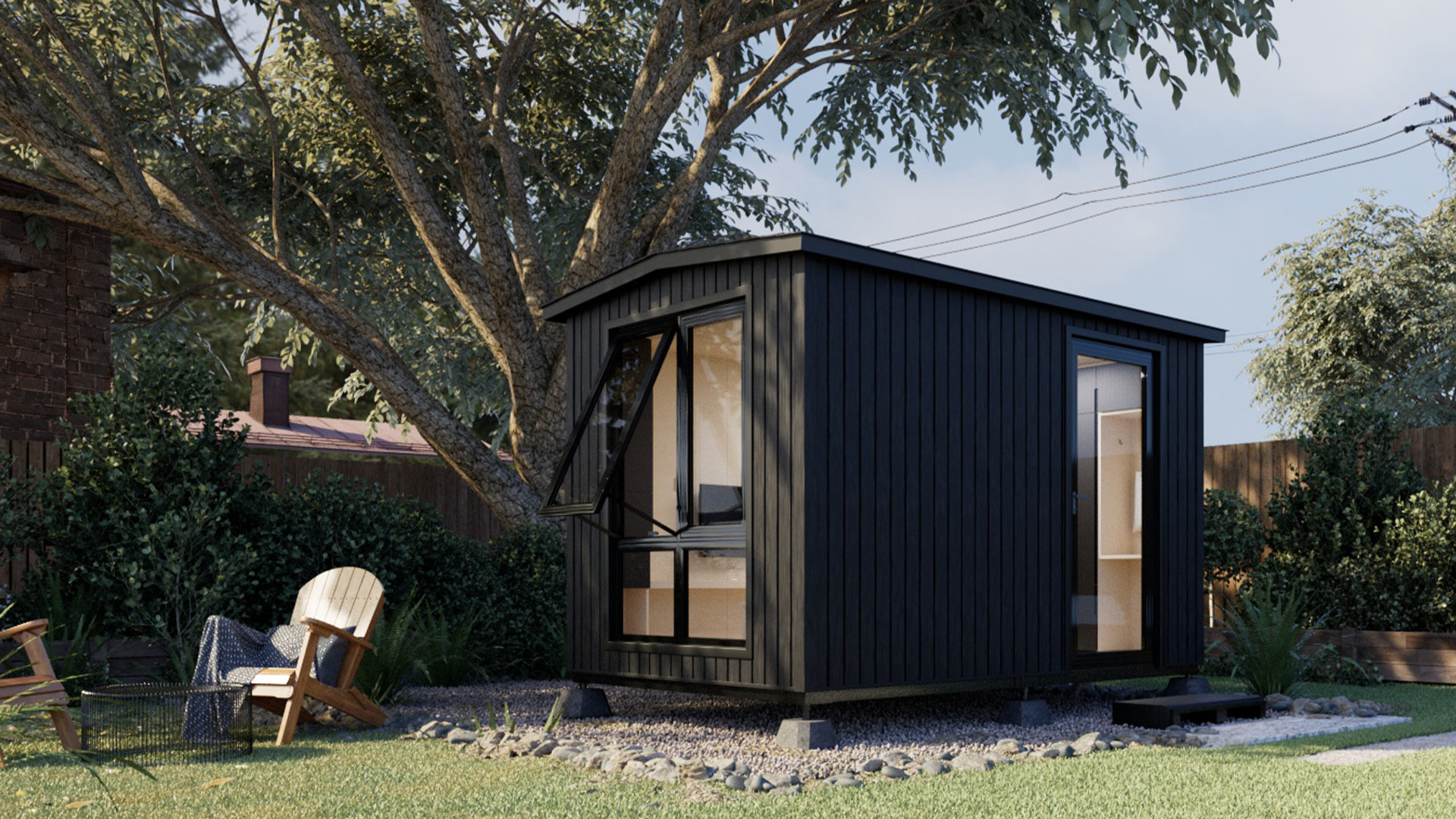

Autonomous WorkPod Versatile
| Dimension | 8’4”W x 12’6”L x 9’10”H |
| Floorspace | 105 square feet |
| Ceiling height | 7’3” |
| Weight capacity | 2.9 tons |
| Pedestal | 18”W x 43”L x 7” |
| Window & door material | Powder-coated aluminum, 5/16” tempered glass |
| Material | Siding: plywood 1/2”, steel frame, honeycomb paper, plywood 3/8”, bitume, housewrap, vinyl siding Roof: roof shingles Floor: plywood Pedestal: steel frame & wood plastic composite |
| Electrical devices | RCB, Wall outlet, Ceiling light switch, Ceiling light, Ventilator switch, Ventilator, Ethernet wall port, 66ft power cable with 2 connectors |
| Include | Optional: Cabinet, Desk, Small & Big Bookshelf, TV Shelf, Foldable Sofa Table, Convertible Sofa Bed. Always included: Electrical Cabinet |
| Power input | Maximum voltage : 110V AC (US standard) Maximum current : 25A Maximum power dissipation : 2750W |
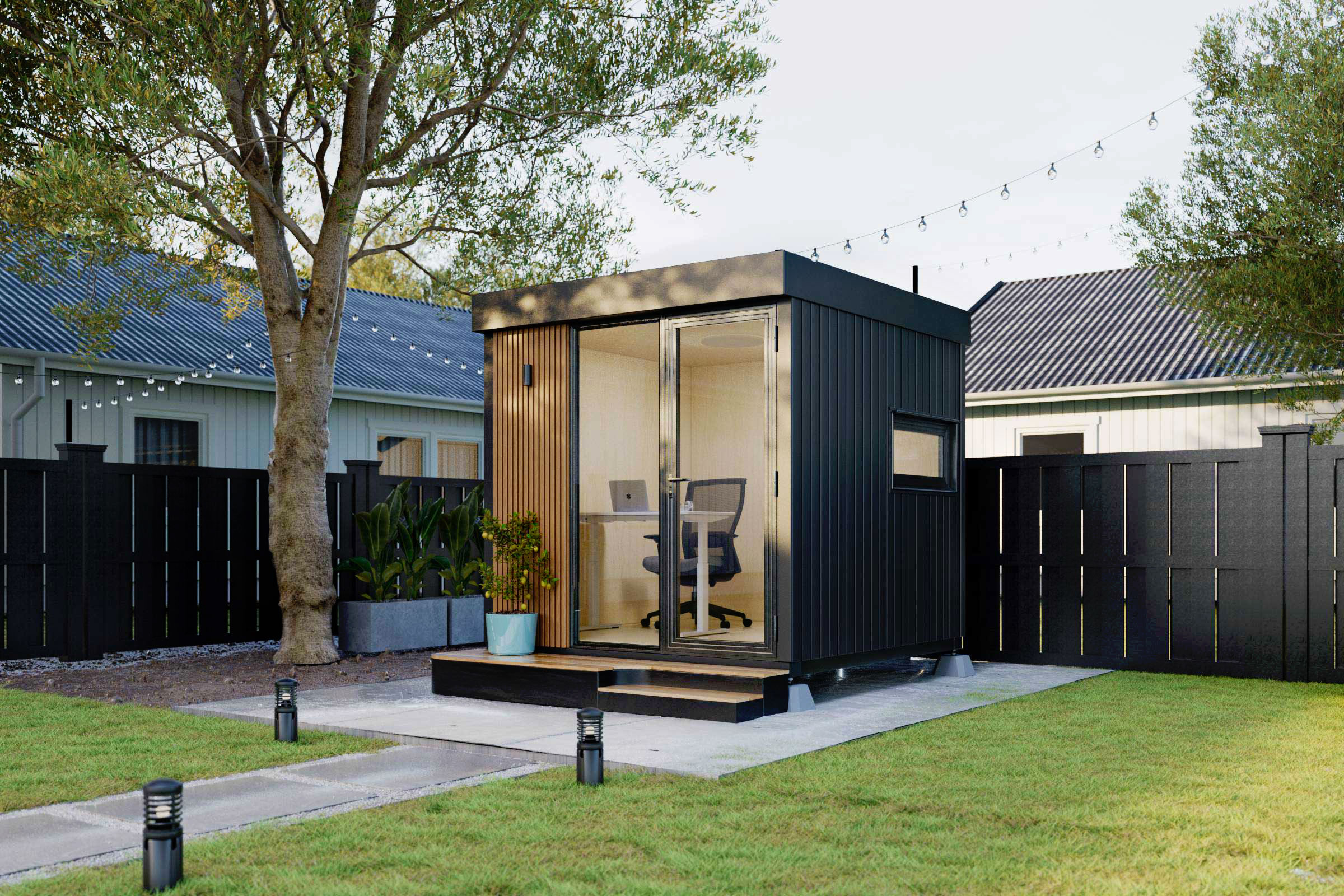
2. Autonomous WorkPod
Now, it is time to discuss the Autonomous Work Pod, a versatile and innovative product designed to enhance productivity and create an efficient workspace. This work pod for homes offers a private and dedicated area for focused work or virtual meetings, making it suitable for remote workers, freelancers, and professionals who need a quiet and distraction-free environment.
One of the standout features of the Autonomous Work Pod is its modular design, allowing for easy customization and flexibility. The pod can be assembled and disassembled extremely fast and without too much hassle, making it portable and convenient for relocation or
reconfiguration. Additionally, the materials used in its construction are durable and of high quality, ensuring longevity and stability, so you can be sure you won't have to change your tiny home in several years.

Autonomous WorkPod
| Dimension | 8’6’’W x 11’9’’L x 11’H |
| Ceiling height | 6’10’’ to 9’4’’ |
| Window material | Wooden frame, 5/16” tempered glass |
| Door material | Anodized aluminum frame, 5/16” tempered glass |
| Material | Siding: bitumen, housewrap, vinyl silding Roof: bitumen, housewrap, shingles roof Floor: plywood Balcony: composite wood |
| Include | Optional: Autonomous Desk, ErgoChair Pro+, Dual Monitor Arm, Cable Tray, Steel Cabinet, Anti-Fatigue Mat. Always included: Electrical Cabinet & Bookshelf |
| Floorspace | 98 square feet |
| Capacity | 2.9 tons |
3. Autonomous WorkPod mini
Finally, the last tiny home on our list is the Autonomous WorkPod mini, a portable and affordable prefab ADU designed to create a focused and efficient workspace for home office workers. It offers a compact solution for those who require a private area to turn into a home office but don't have enough space in their own homes.
Moreover, our WorkPod mini features a modular design, allowing easy assembly and disassembly. This makes it highly portable and convenient for relocation or storage. The pod is built using sturdy and durable materials that ensure stability and longevity.
Despite its compact size, the WorkPod mini offers essential amenities to support productivity and comfort. These amenities include a spacious desk with enough room for a laptop or other work essentials. The pod also provides integrated power outlets and cable management solutions to keep the workspace organized and clutter-free. It might be a bit small for housing, but it definitely serves its purpose as a portable home office.

Autonomous WorkPod mini
| Dimension | 8.7"W x 8.12"L x 9.3"H |
| Material | Window and door: powder-coated aluminum, 5/16-inch tempered glass Siding: plywood 1/2-inch, steel frame, honeycomb paper, plywood 3/8-inch, bitume, housewrap, vinyl siding Roof: metal roofing Floor: plywood Balcony and Pedestal: steel frame and wood plastic composite |
| Pedestal | 24"W x 103"L x 9"H |
| Electrical devices | RCB, Wall outlet, Ceiling light switch, Ceiling light, Wall light, Ethernet wall port, 66ft power cable with 2 connectors |
| Weight capacity | 2.3 tons (including Pod body) |
| Floorspace | 80 square feet |
| Ceiling height | 7.3-inch |
Bottom Line
In conclusion, navigating the world of tiny house zoning regulations is crucial for anyone interested in embracing the tiny house lifestyle. Zoning regulations play a significant role in determining where and how tiny houses can be located, and they vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another. Understanding the specific zoning laws and building codes in your desired location is essential to ensure compliance and avoid legal complications.
By conducting thorough research, consulting local authorities, and seeking professional guidance, you can navigate the complexities of zoning for tiny houses and find a suitable place to call home. This means that with the proper knowledge and preparation, you can confidently embark on your tiny house journey, embracing the freedom, simplicity, and sustainability of tiny living.
.svg)