Stool vs. Chair: Which is Better for Your Comfort?
Table of Contents
When setting up a workstation, one of the most important decisions you’ll make is choosing the right seating. For many, this comes down to the age-old debate: are stools better than chairs? Whether you’re looking for comfort, ergonomics, or space efficiency, both stools and chairs offer unique benefits. In this article, we’ll break down the difference between a stool and a chair, dive into stool vs chair posture, and compare ergonomics, comfort, and productivity in both.
1. Understanding the Stool
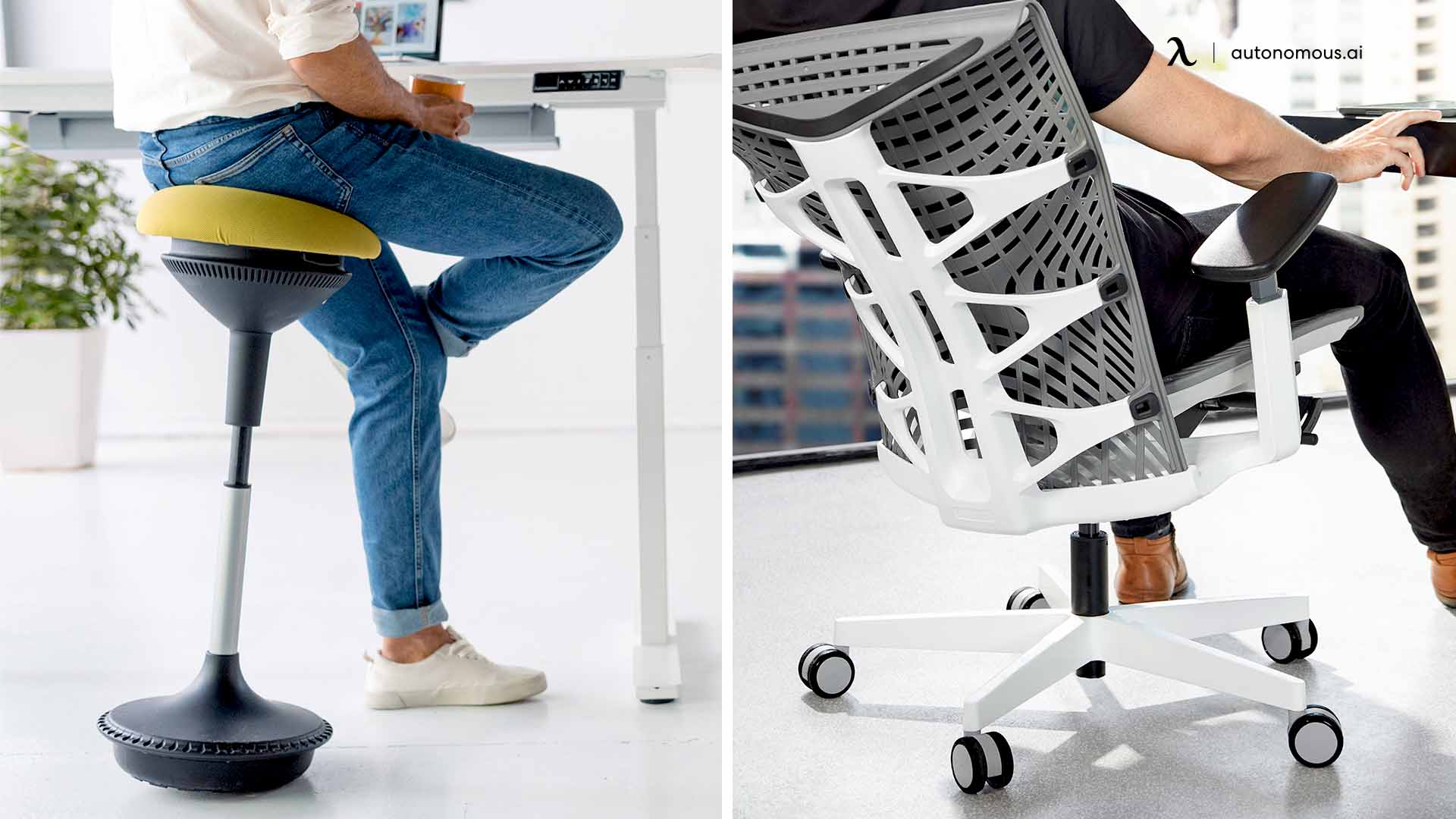
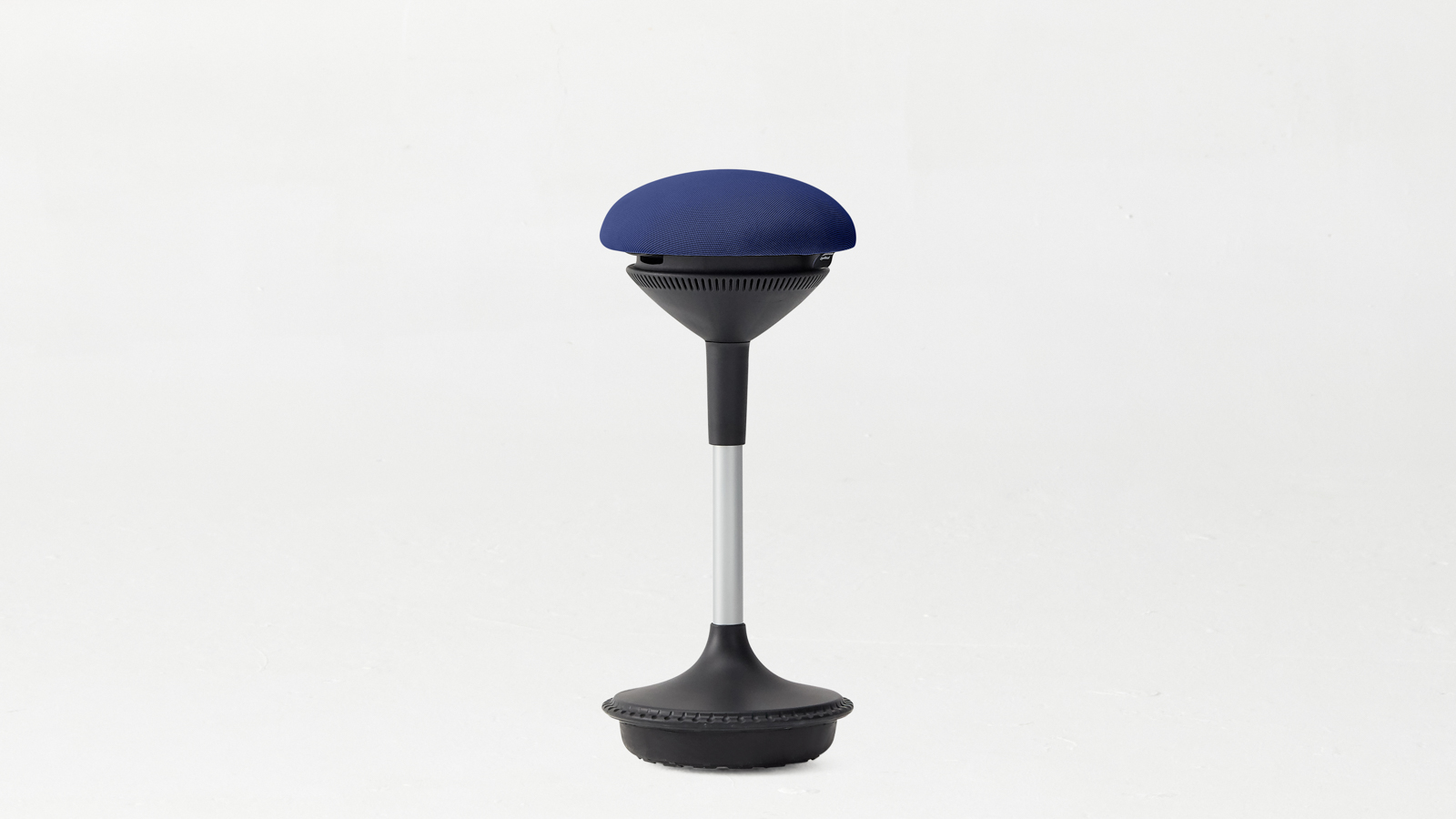
A stool is typically a backless, minimalist seating option ideal for short-term use. It usually has 3 or 4 legs, and some stools feature adjustable height or a swivel mechanism, especially drafting stools. Stools are commonly used in environments where mobility and space-saving are a priority.
- Space-Saving
Stools are perfect for compact workspaces or casual setups. They take up less space than traditional office chairs, making them great for smaller rooms or flexible environments.
- Active Seating
A stool encourages movement, which can help reduce stiffness. Sitting on a stool promotes better circulation and keeps you more engaged in your work. Active sitting can improve your overall comfort during the day.
- Quick and Easy
Perfect for quick tasks or environments where you need a versatile seating solution. Stools are lightweight and easy to move around, making them ideal for flexible workspaces. If you're looking for a better ergonomic experience for your sitting routine, active seating could be a great option.

2. Understanding the Chair
A chair, on the other hand, typically features a backrest and sometimes armrests, offering far more support than a stool. Ergonomic chairs, in particular, are designed with long-term comfort and posture in mind, with adjustable height, lumbar support, and other customizable features.
- Improved Comfort
Ergonomic office chairs offer better cushioning and back support, especially for long hours of work or gaming. If you want additional comfort, consider an office chair with adjustable seat depth to ensure you’re seated at the ideal position for your body.
- Posture Support
An ergonomic chair helps you maintain proper posture, reducing strain on your back and neck. An office chair with adjustable arms and office chair with adjustable lumbar support can further enhance posture support, ensuring you’re seated comfortably and healthily.
- Ideal for Long Hours
A chair, especially an ergonomic office chair, is a better option for those who spend long hours working at their desk. For added neck and head support, consider an office chair with headrest or a reclining ergonomic chair that allows you to take breaks and adjust your sitting position throughout the day.
Additionally, if you prefer to keep your feet elevated, an ergonomic chair with footrest can provide extra comfort and relieve pressure on your legs.

3. Stool vs Chair: Comfort and Posture
One of the most significant differences between a stool and a chair is how they affect your posture and comfort over time.
3.1. Stool vs. Chair Posture
Sitting on a stool vs chair often results in very different experiences. Stools generally lack the support of a backrest, meaning you’re more likely to slouch or lean forward. In contrast, chairs, particularly ergonomic options, encourage a neutral spine position and provide lumbar support to maintain a healthy posture. Stool vs chair ergonomics shows that a chair is the better choice for reducing back pain during long periods of sitting. For better support, an office chair for back support or a desk chair for upper back pain will help align your spine. Additionally, if you need to understand the parts that contribute to the support, you can check the office chair parts diagram for more insights.
For those specifically dealing with lower back discomfort, ergonomic chair for lower back pain is a great solution to ensure proper support.
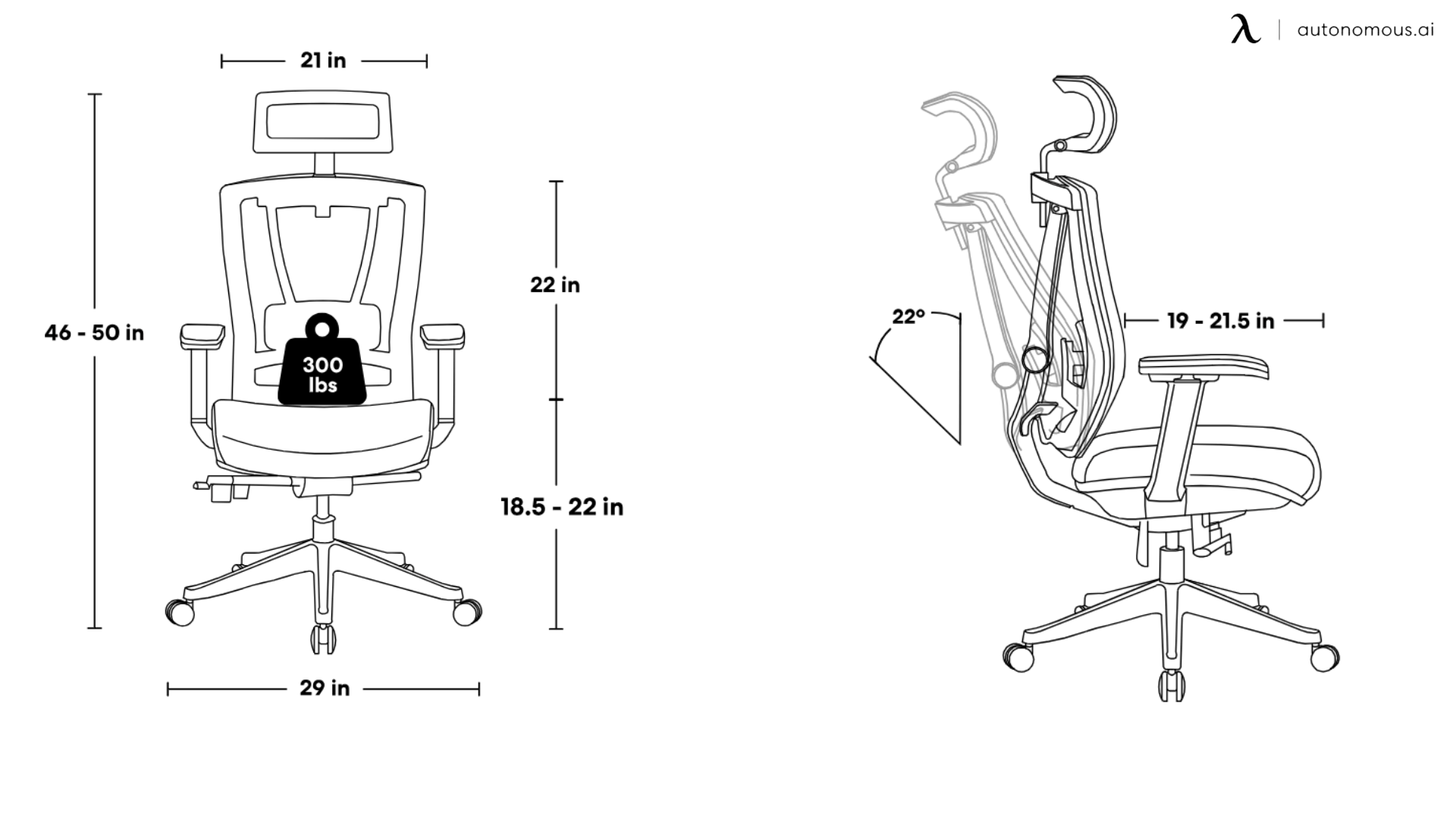
3.2. Stool vs. Chair for Desk
If you’re working at a desk for extended periods, sitting on a stool vs chair can affect your focus and productivity. While stools are great for quick tasks or moving around, chairs are designed for better posture, offering lumbar support and cushioning to reduce strain during long work hours. For those using a height adjustable standing desk or a small standing desk, a chair can help maintain proper alignment throughout the day. On the other hand, stools, especially an ergonomic stool for standing desk, can provide a more active sitting option when you need to switch between sitting and standing.
For a standing desk setup, it’s crucial to have the right balance between comfort and posture. Explore our guide for an ideal standing desk setup for tips on optimizing your workspace.
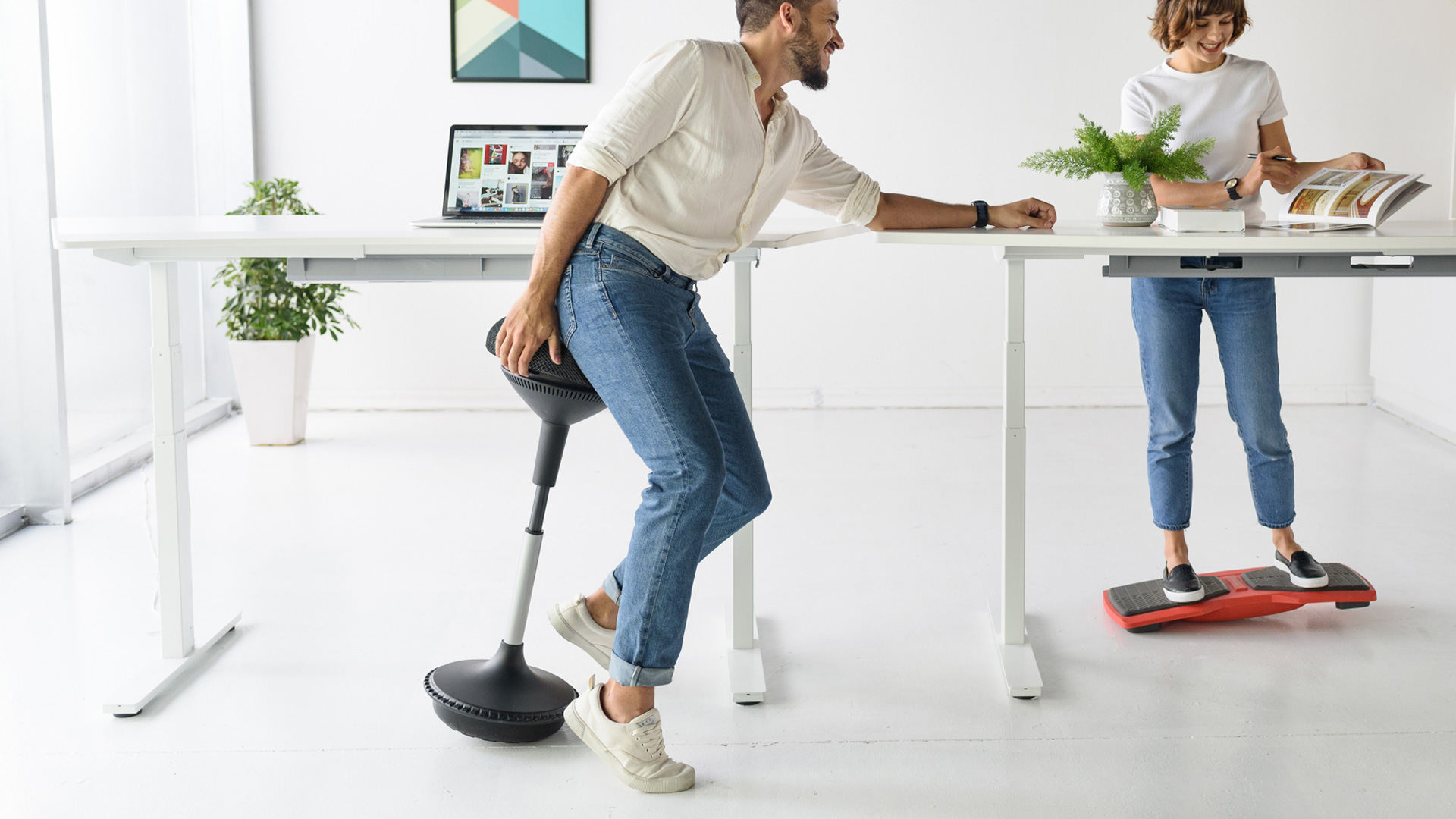

4. Drafting Stool vs Office Chair
When comparing drafting stools vs office chairs, drafting stools are often more adjustable in height, making them ideal for standing desks or high tables. However, they usually lack back support, which makes them less suitable for long hours of desk work. Office chairs, in contrast, are designed to provide support for extended sitting sessions and are more adjustable to ensure comfort throughout the day. If you're considering a drafting chair, it can be a great solution for high surfaces but might not provide the same level of comfort as an office chair for long hours.
.webp)
5. When to Choose a Stool or Chair
The decision between a stool and a chair depends on the type of work, comfort needs, and the environment you're in. Stools are great for casual workstations, especially when you need flexibility, a compact option, or more mobility. They're perfect for short tasks, limited space, or when you want to encourage active sitting. However, stools may not be suitable for long hours of sitting, as they lack back support.
On the other hand, chairs are the better choice for long hours of sitting, especially if you need lumbar support or have health concerns such as back pain. An ergonomic office chair ensures proper posture and provides the comfort needed for sustained work or gaming. If you're in a professional environment, an office chair offers the necessary support to stay productive throughout the day, making it ideal for extended periods at a desk.
Feature | Office Stool | Office Chair |
Design | Backless, compact, lightweight. | Full backrest with adjustable features. |
Height Adjustability | Often adjustable for higher desks or workstations. | Adjustable for various desk heights. |
Support | Limited back support, usually no lumbar support. | Provides lumbar support, full backrest support. |
Mobility | Encourages movement, ideal for quick tasks. | Less mobile, better for stationary sitting. |
Comfort | Less comfortable for long sitting, especially without padding. | Designed for comfort over long hours. |
Ergonomics | Generally lacks ergonomic features. | Designed with ergonomic adjustments to support posture. |
Posture Support | Can lead to slouching and poor posture. | Supports proper posture with adjustable backrest and lumbar support. |
Suitability | Ideal for short, active sitting, and limited space. | Best for long periods of sitting, especially at desks. |
Space Efficiency | Takes up less space, ideal for small setups. | Requires more space, particularly with armrests. |
Best For | Casual work, tight spaces, active sitting. | Professional workstations, extended sitting, and comfort. |
Examples | Drafting stools, bar stools, and drafting chairs. | Ergonomic office chairs, task chairs, executive chairs. |
6. FAQs
Q: Are stools better than chairs for posture?
A: While stools can promote active sitting by encouraging movement, office chairs are generally better for maintaining proper posture over long periods due to their built-in backrest and lumbar support.
Q: Can I use a stool at my desk for long hours?
A: While stools can be ideal for short tasks or standing desk setups, they lack the comfort and support needed for extended sitting. For long hours of desk work, a chair with lumbar support is recommended.
Q: Which is better for a small space, a stool or chair?
A: A stool is typically a more space-efficient option compared to a traditional office chair, as it takes up less room and can be easily stored when not in use.
Q: Are stools more ergonomic than office chairs?
A: Stools can be more ergonomic if they are designed for active sitting, but traditional office chairs generally provide better support for long-term sitting, with adjustable features to cater to your posture needs.
Q: Can a drafting stool replace an office chair?
A: Drafting stools are great for high desks or standing desks, but they may not provide the level of comfort and support that an office chair offers, especially for long hours of work.
Q: Should I use a stool or a chair for gaming?
A: For gaming, comfort is key, and an office chair with ergonomic features like lumbar support is usually the better choice for long gaming sessions. Stools may lack adequate back support for extended periods of sitting.
Conclusion
In the stool vs chair debate, the right choice depends on your specific needs. For short tasks or space efficiency, a stool can be a great option. However, for long periods of sitting or to ensure better posture and comfort, a chair—especially an ergonomic model—will be your best bet. Consider the nature of your work and your physical needs when deciding whether a stool or chair is right for you.
Spread the word
.svg)