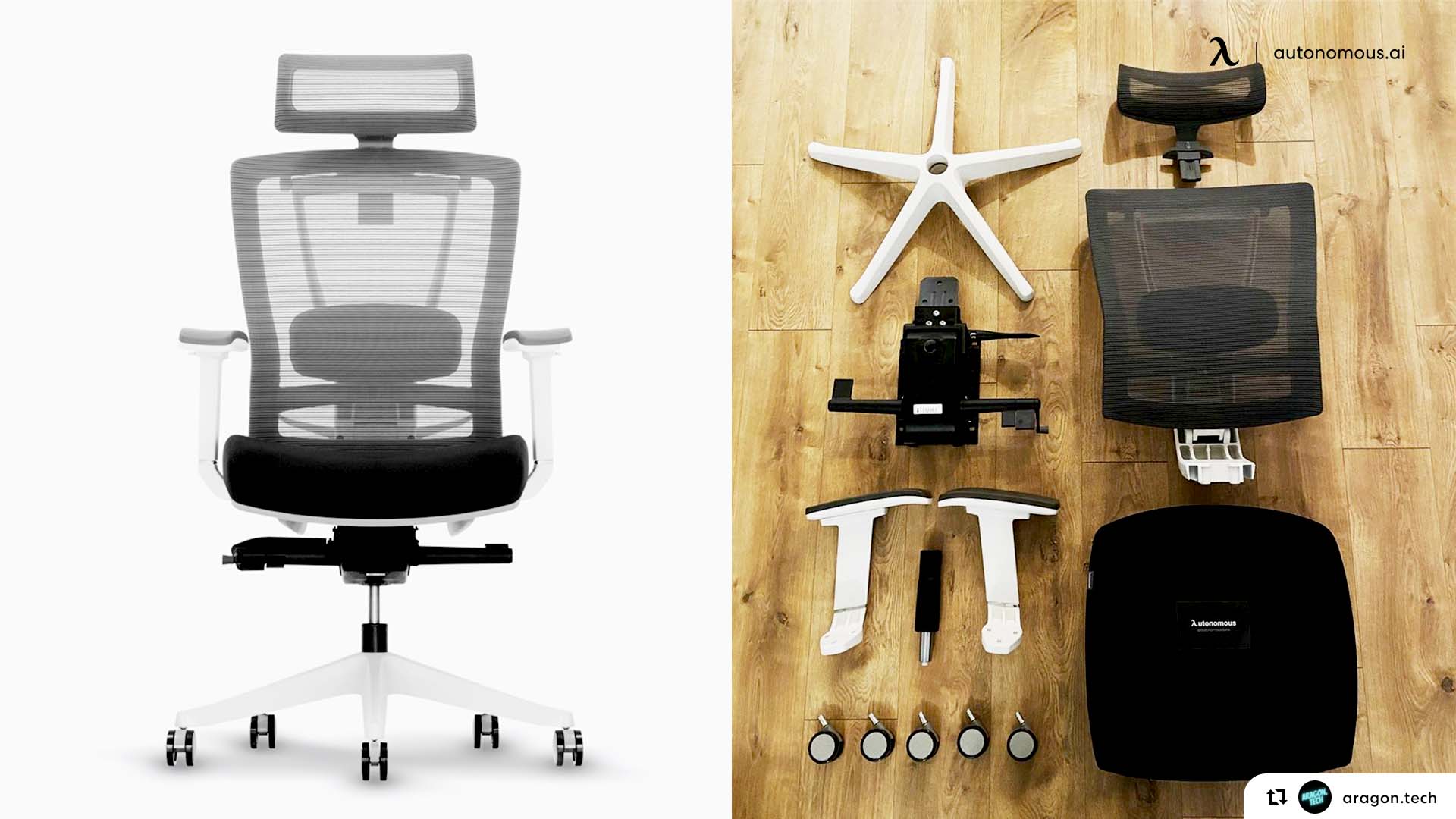
Ultimate Guide To Explore 9 Essential Parts Of A Chair
Table of Contents
Knowing the parts of a chair is key to selecting the right office chair for your needs and ensuring it supports your comfort and productivity. From the seat cushion to the gas lift, each component plays a role in your chair’s functionality.
Familiarizing yourself with different parts of a chair helps you make informed decisions, whether you're adjusting your chair for the perfect fit or looking to maintain it properly. In this guide, we'll break down the essential parts of a chair and how they contribute to a better seating experience.
Understanding Parts Of A Chair Diagram: Why It Matters
Getting to know the parts of a chair diagram goes beyond just a fun DIY project—it’s a smart way to enhance your chair’s performance and extend its lifespan.
When you take a closer look at parts of a chair diagram, you'll see how each component, such as the casters, armrests, and lumbar support, plays a crucial role in the chair's overall functionality. Familiarizing yourself with the names of parts of a chair will make it easier to carry out basic maintenance and repairs on your own.
Here are some key benefits:
- Prolongs Lifespan:
By recognizing which parts of a chair need attention, like worn-out casters or a dirty tilt mechanism, you can address issues early, preventing expensive repairs or replacements down the road.
- Saves Money:
With a clear diagram, small repairs like replacing casters or tightening screws become simple tasks that you can handle yourself, avoiding costly professional services.
.webp)
- Improves Comfort And Productivity:
Understanding how to adjust components like seat height and lumbar support ensures your chair fits you perfectly, improving posture, reducing discomfort, and helping you stay focused for longer.
- Promotes Sustainability:
Instead of discarding your chair when something goes wrong, diagrams allow you to replace individual parts, reducing waste and contributing to a more sustainable choice.
Incorporating diagrams into your chair maintenance routine is an easy yet effective way to make your chair last longer and work better for you.
Parts Of A Chair Diagram: A Visual Breakdown
1. Office Chair Base
The base is the foundation of your chair, designed to provide stability and support. It consists of the five-star structure or sometimes a more compact base, which holds the casters and connects to the gas lift cylinder. The base helps distribute weight evenly to prevent tipping and ensures your chair stays balanced.
Different Types of Office Chair Base:
- Steel:
Known for its heavy-duty durability, steel bases are ideal for users seeking robust support in a heavy-duty office chair. They can handle higher weight capacities and provide long-lasting strength, making them the best option for heavier users or those who require long-term stability.
- Aluminum:
Lightweight and less prone to rust, aluminum provides a good balance between mobility and strength. It’s a common choice for chairs that need easy maneuverability, like drafting chairs or adjustable-height chairs.
- Polypropylene:
Polypropylene is a more budget-friendly material that is commonly used in lighter executive office chairs. Though it’s cost-effective and portable, it may not offer the same level of durability as steel or aluminum, making it less suitable for heavier users.
Signs They Need Replacement:
- Visible cracks or damage: A cracked base can lead to instability and should be replaced immediately.
- Wobbly chair: If your chair feels wobbly or unstable, the base may be deteriorating. This is especially a concern if the casters are no longer secure.
Tip: If you’re dealing with a chair that’s showing signs of base wear, consider upgrading to a steel or aluminum base for added durability and support. Avoid using lightweight bases for heavy-duty use.
2. Office Chair Mechanism
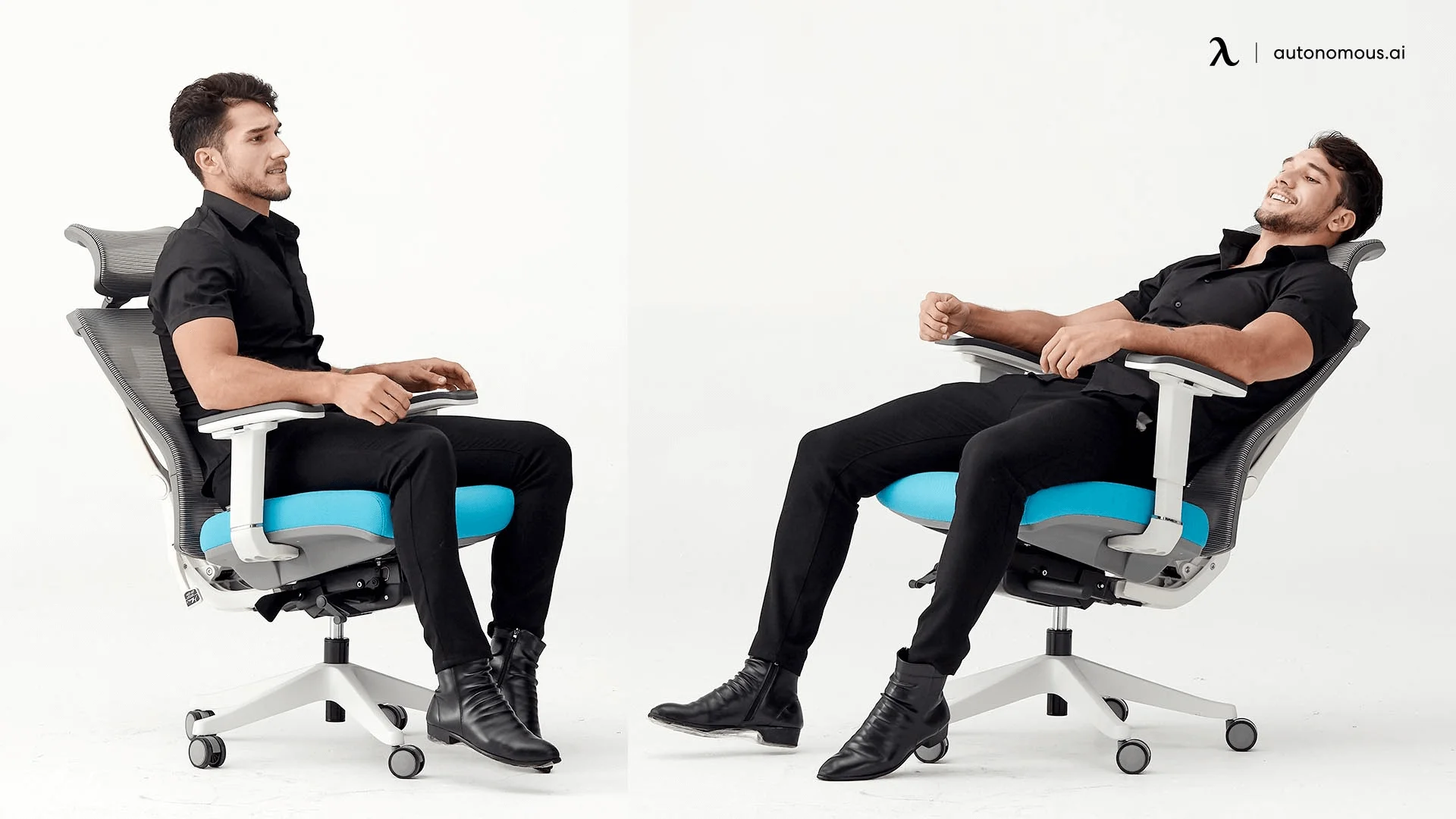
The office chair mechanism controls the adjustments your chair can make. Located underneath the seat pan, the mechanism allows for changes in seat height, tilt, recline, and backrest angle, offering a customizable seating experience.
What It Includes:
- Tilt Mechanism: This allows the seat to recline, giving you the option to change your posture and reduce strain during long working hours. For better posture, some chairs also offer a forward tilt feature, which encourages a more ergonomic seating position.
- Height Adjustment: The mechanism that lets you raise or lower the seat to find the most comfortable sitting position, ensuring that your feet are flat on the floor and your desk height is optimal.
- Recline Lock: This feature locks the backrest at a specific angle to prevent unintended movement, keeping you comfortable without worrying about the chair reclining too far. Different chair tilt lock mechanisms can provide varying degrees of recline and locking functionality to suit your preferences.
- Tension Control: Adjusts the resistance of the tilt, so you can make the chair easier or harder to recline depending on your preference.
Signs They Need Replacement:
- Unresponsive height or tilt adjustments: If your chair no longer raises or tilts smoothly, the mechanism might be worn out.
- Difficulty locking the backrest: If the tilt lock no longer holds your chair in place, it’s time to check the mechanism for wear or damage.
Tip: Regularly maintain the mechanism by cleaning it to remove dust or debris, which could cause it to function poorly. For better comfort, opt for a chair with a synchro-tilt mechanism that allows the seat and backrest to move together, promoting better posture.

3. Seat Pan
The seat pan is the part of the chair you sit on. It’s the flat surface that connects to the base and supports the seat cushion. A well-designed seat pan with high-quality chair seat materials ensures that you’re seated properly, preventing discomfort that could arise from poor seating posture.
Different Types of Seat Pan:
- Standard Seat Pan: A basic, flat seat that provides foundational support. It’s ideal for those looking for a straightforward, no-frills chair.
- Molded Seat Pan: These molded seats offer a more customized fit, providing additional comfort and support, especially for long sitting sessions.
- Cooling Seat Cushion: If you're prone to heat discomfort, adding a cooling seat cushion can help regulate temperature and keep you comfortable for longer periods.
- Memory Foam Seat Cushion: For enhanced comfort and pressure relief, a memory foam seat cushion molds to your body, offering personalized support and helping reduce discomfort during extended sitting.
Signs They Need Replacement:
- Discomfort: If your seat pan feels flat or uncomfortable, it might be time to replace it or add cushioning for better support.
- Loss of shape or padding: If the cushion or seat pan has flattened, it will no longer provide adequate comfort or ergonomic support.
Tip: Consider an office chair with a cushion made from high-density foam or memory foam for added comfort, especially if your seat pan is hard or too firm.
.webp)
4. Gas Lift Cylinder (Height Adjustment Mechanism)
The gas lift cylinder connects the seat pan to the chair base and is responsible for enabling height adjustments. It uses a gas spring to allow you to raise or lower the chair for optimal ergonomics.
How It Works:
When you pull the lever, gas is released from the cylinder, allowing the seat to move up or down smoothly. The gas lift ensures you can adjust your height with minimal effort and maintain proper posture by aligning the chair with your desk.
Signs They Need Replacement:
- Chair sinks when seated: If your chair begins to sink or won't stay at the desired height, the gas lift cylinder might be damaged.
- Inability to adjust height: If the height adjustment lever doesn’t respond, the cylinder may be worn out.
Tip: Before replacing the gas lift, check for blockages or debris that might be preventing smooth movement. If replacement is necessary, ensure you purchase a compatible cylinder that matches your chair's design.
.webp)
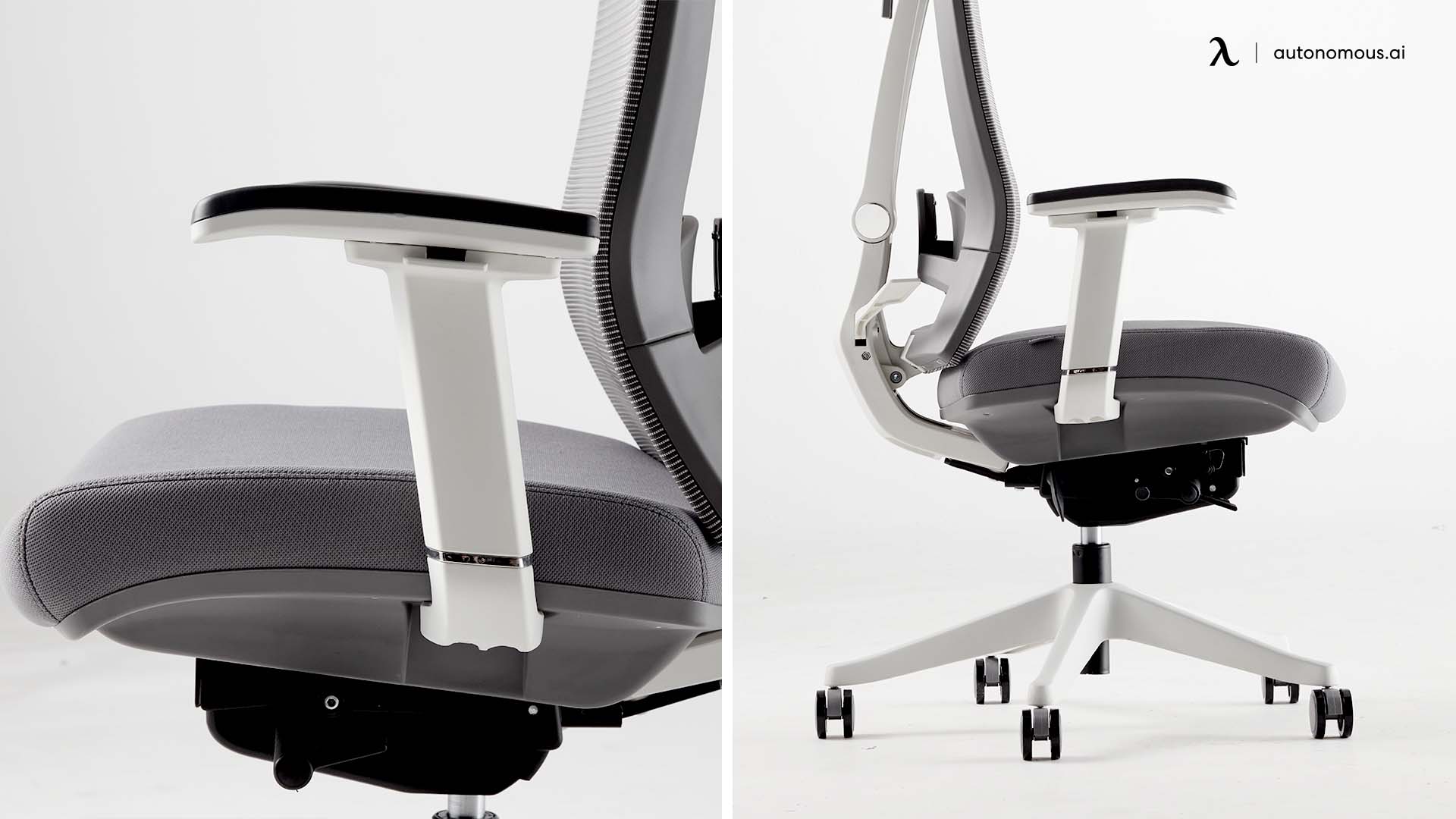
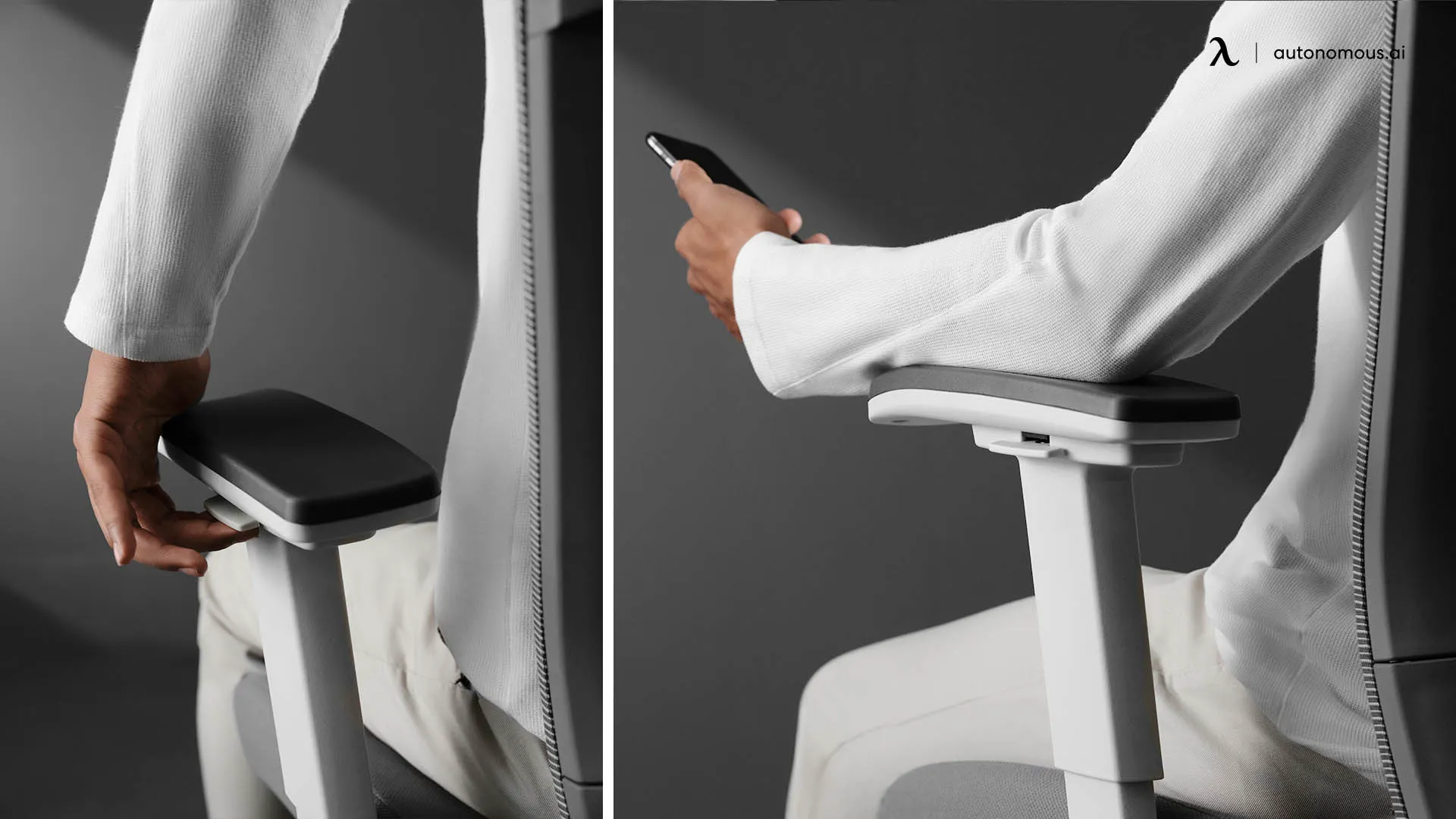
5. Armrests
Armrests support your arms and shoulders while seated, helping to reduce strain and improve posture. They allow you to rest your arms while typing, writing, or using a mouse.
Different Types of Armrests:
- Fixed Armrests: These are stationary and provide basic support. They are often found on budget chairs.
- Adjustable Armrests: Office chairs with adjustable armrests allow you to change the height and width of the armrests to suit your comfort level.
- Flip-Up Armrests: An office chair with flip-up arms that can be raised and moved out of the way, allowing for greater mobility and convenient storage. This design adds flexibility to your workspace.
- T-Armrests: T-Armrests provide excellent support and customization, making them ideal for prolonged use. Advanced options, like those 4D armrest office chairs, allow adjustments in height, width, depth, and angle for superior ergonomic functionality.
- No Armrests: For those who prefer a minimalist design or need more space, an armless office chair is an excellent alternative. These chairs provide more freedom of movement and are ideal for compact workstations.
Signs They Need Replacement:
- Loose or wobbly armrests: If the armrests are shaky or don't stay in place, they may need tightening or replacement.
- Worn-out padding: If the armrests feel uncomfortable or the padding has flattened, it's time to replace them.
Tip: For better ergonomic support, look for adjustable armrests, which allow for a customizable fit, reducing the strain on your shoulders and neck.

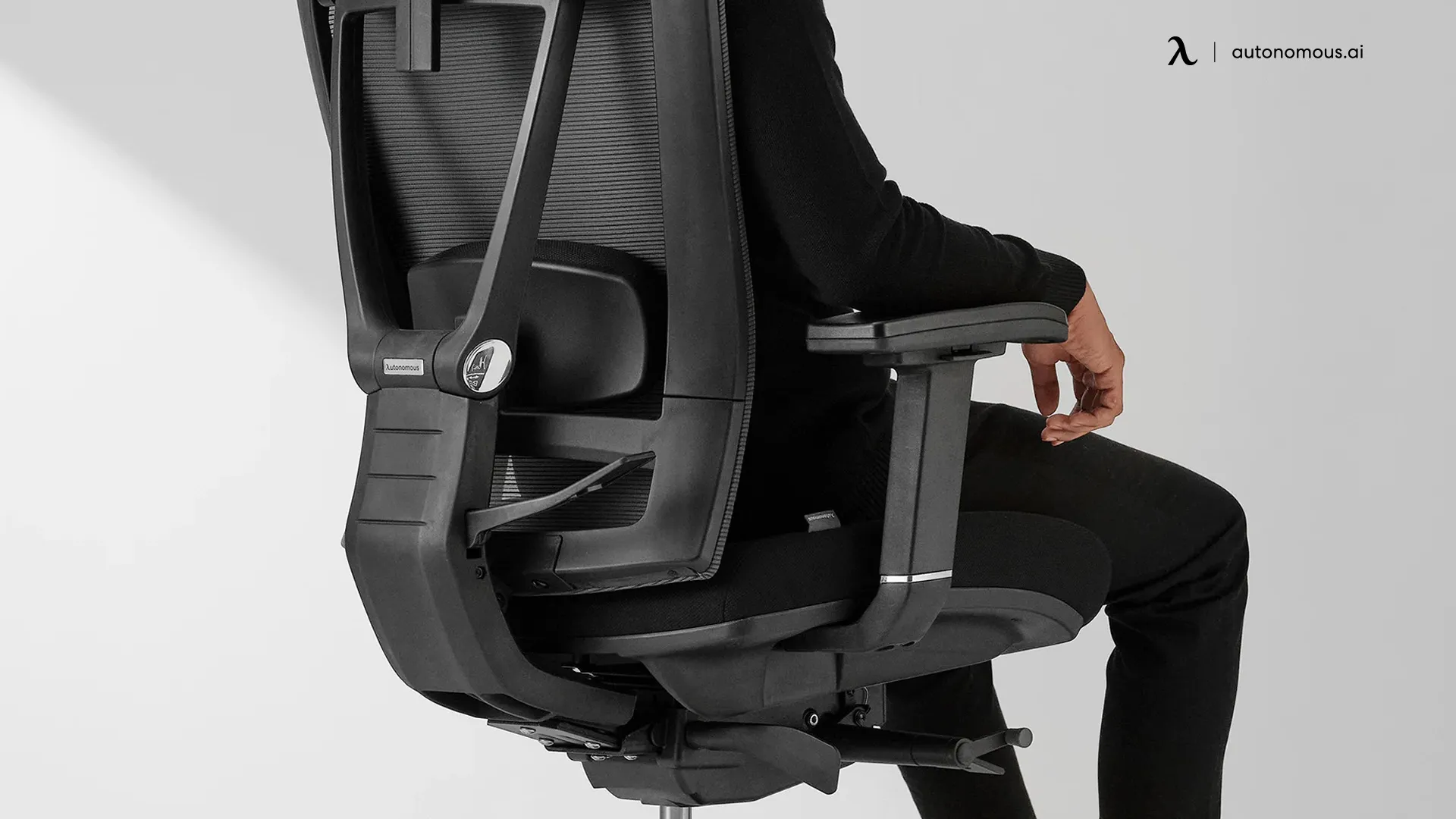
6. Lumbar Support System
Lumbar support is integrated into the backrest of the chair to support the lower back and maintain the spine’s natural curve. An ergonomic office chair with lumbar support can significantly reduce strain on the lower back and promote good posture, especially during long hours of sitting.
Tip: Adjust the lumbar support to fit the curve of your lower back. If your chair lacks lumbar support, consider adding a cushion for additional relief. To learn more about where lumbar support should be positioned for optimal comfort, check out this guide on where lumbar support should be positioned.
Signs They Need Replacement:
- Lack of support: If the lumbar support is no longer providing relief or is uncomfortable, it may need adjustment or replacement.
- Persistent back pain: If you experience lower back pain regularly, the lumbar support might not be positioned correctly or needs replacement.

5. Backrest
The backrest provides support to the upper and lower back, helping to maintain posture and prevent discomfort. A well-designed backrest is crucial for reducing pressure on the spine and providing comfort during long hours of sitting.
Signs They Need Replacement:
- Unstable or wobbly backrest: If the backrest moves too much or feels loose, it may need to be tightened or replaced.
- Lack of proper support: If the backrest no longer supports your back adequately, it’s time for a replacement.
.webp)
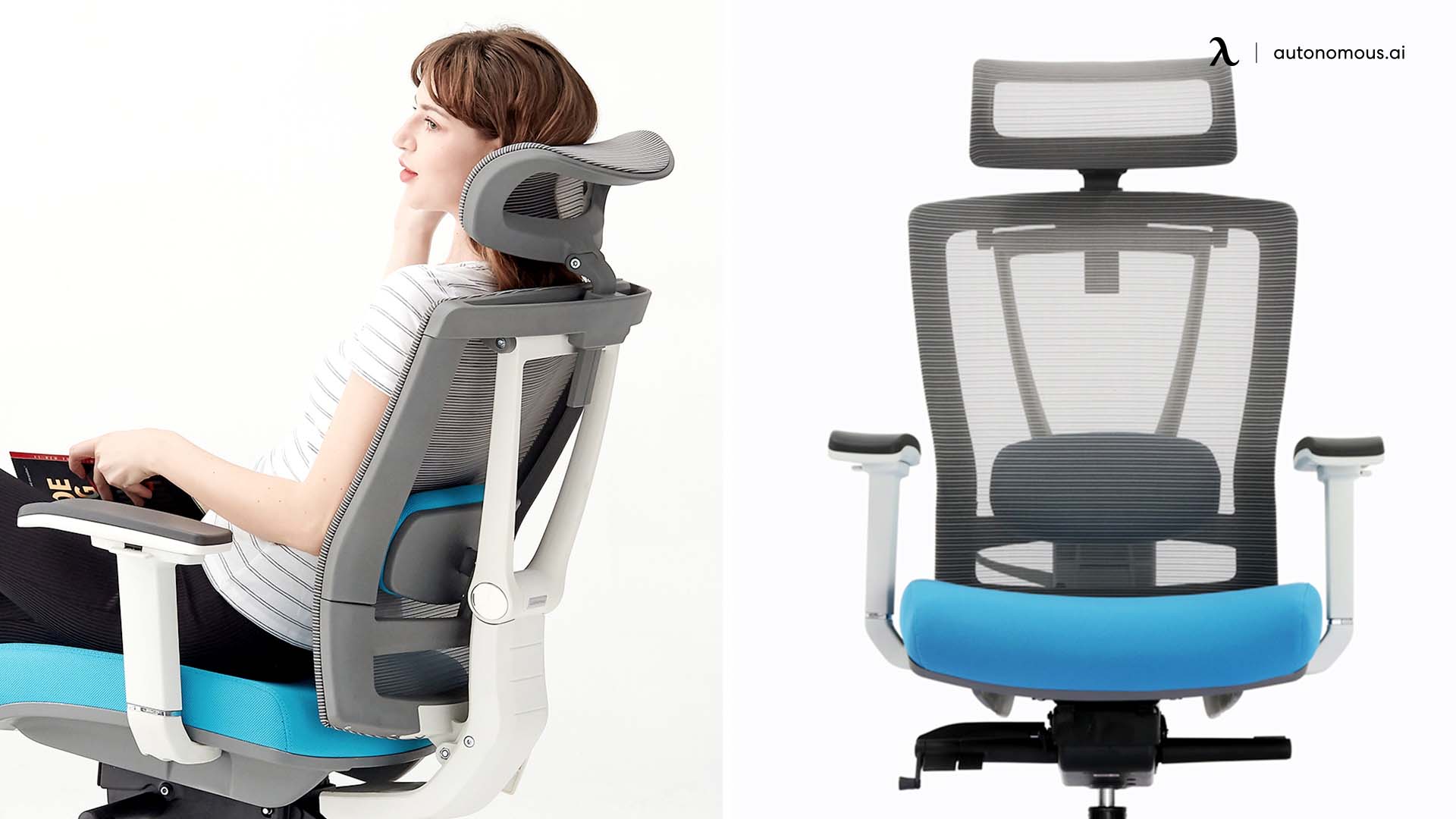
8. Headrest
An office chair with a headrest provides support for your neck and head, helping to reduce strain, especially for those who spend long hours sitting.
Signs They Need Replacement:
- Neck pain: If the headrest no longer supports your neck properly, you may experience discomfort or strain.
- Loose or broken mechanism: If the headrest moves out of position or doesn’t stay in place, it might need to be repaired or replaced.

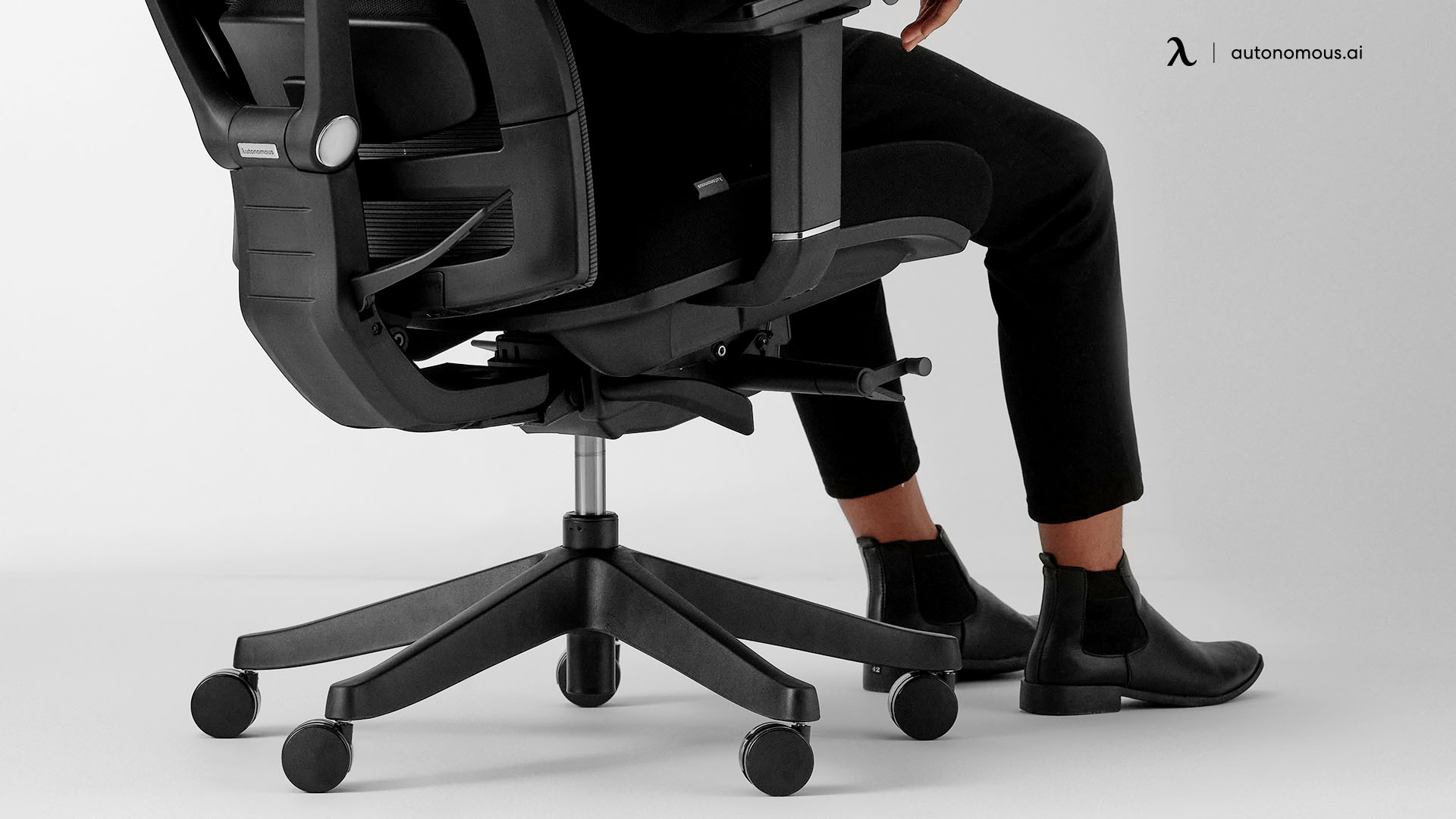
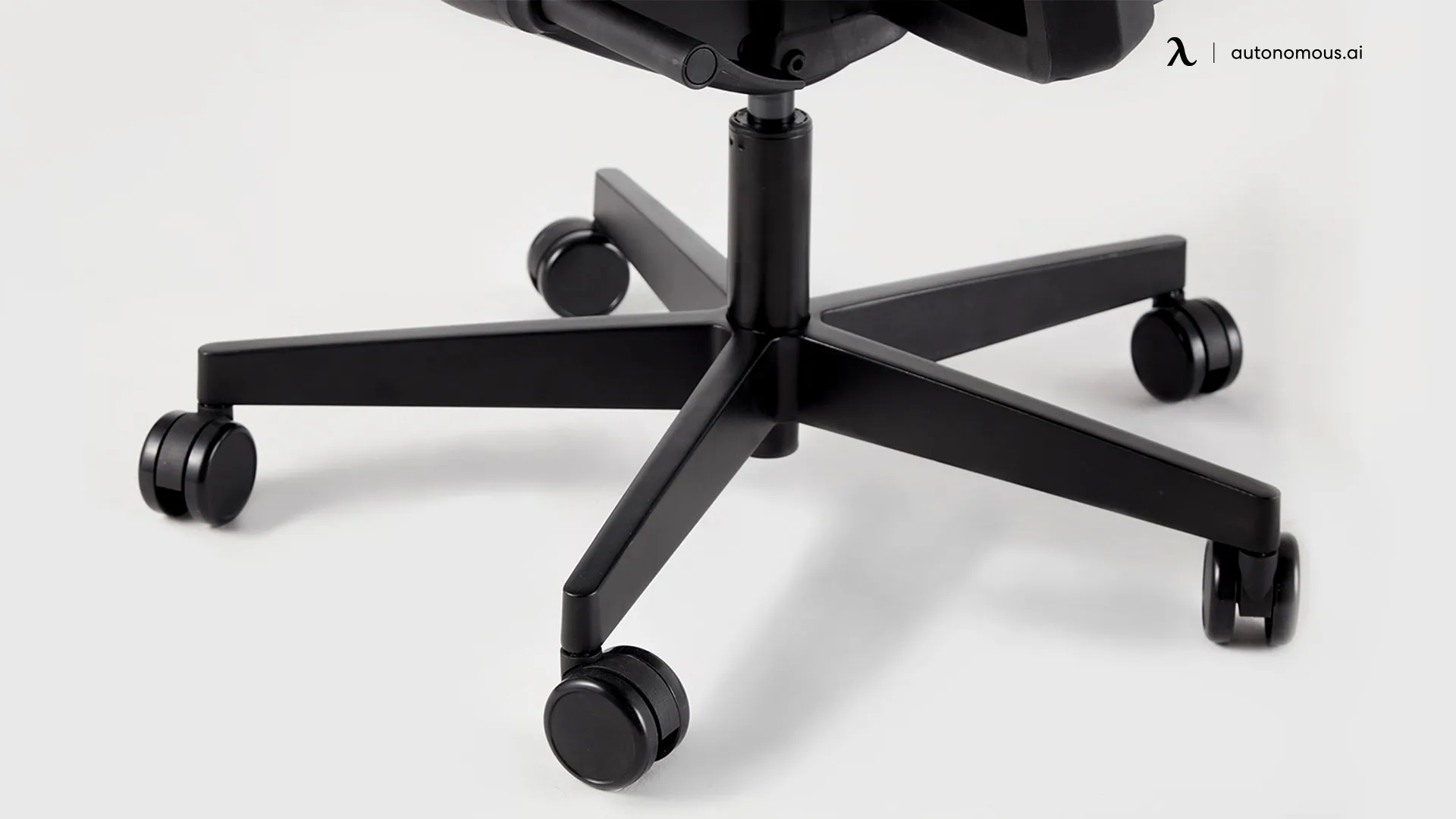
9. Casters (Wheels)
Casters are the wheels attached to the base of your chair, providing mobility and allowing you to move freely across the floor.
Types of Casters:
- Soft Casters: Ideal for hard floors like tile or hardwood, soft casters prevent scratches and allow for smooth rolling.
- Hard Casters: Best for carpeted floors, hard casters offer better resistance and allow the chair to roll easily over fabric surfaces.
When choosing between soft and hard casters, it’s important to consider the type of flooring in your workspace. Soft casters are designed to protect hard floor surfaces, providing a smoother glide, while hard casters are optimized for carpeted areas, offering better traction.
In addition to casters, you may also come across glides, which serve a different purpose. While casters allow your chair to roll, glides keep it stationary. If you're interested in understanding the differences between glides and casters, check out our guide on office chair glides and casters.
Signs They Need Replacement:
- Squeaky or stuck wheels: If the casters are making noise or won’t roll smoothly, they may need cleaning or replacement.
- Floor damage: If the wheels are scratching or damaging your floor, it might be time to switch to softer casters or replace worn-out ones.

Identifying Common Office Chair Issues
Maintaining your office chair regularly is essential to ensure its longevity and keep it functioning properly. By learning to recognize when parts need replacement and using a parts of a chair diagram, you can prevent discomfort and avoid costly repairs.
Let’s explore some common office chair issues and how you can easily identify and fix them.
- Difficulty Moving the Chair: If your chair no longer rolls smoothly, there could be an issue with the casters or wheels. If hair or debris is stuck in your wheels, it can affect the chair's movement. Simply removing hair stuck in the office chair wheels will fix the problem quickly with no hassle.
- Squeaky or Unstable Components: Unusual noises or instability may point to worn-out parts, such as loose screws or damaged mechanisms.
- Loss of Comfort: When your chair no longer provides the comfort it once did, it may be due to worn-out padding or seat cushion degradation.
- Malfunctioning Adjustment Mechanisms: If your chair’s height, tilt, or recline functions are no longer responsive, there might be a problem with the adjustment mechanisms.
How To Replace Office Chair Parts
Replacing office chair parts is straightforward, especially for smaller components like casters and armrests. Here’s how to do it:
- Identify the Part: Determine which part needs replacing, such as the casters, gas lift cylinder, or seat cushion.
- Check with the Manufacturer: Contact the manufacturer to find replacement parts. They may sell them directly or through authorized retailers.
- Replacing Small Parts: Small parts like chair casters and armrests are easy to replace. They usually snap or screw into place, making DIY replacement simple.
- Replacing Larger Parts: For larger components like the gas lift cylinder, you may need tools such as a wrench. In some cases, professional help may be needed if the chair’s core mechanism needs disassembly.
By understanding the process and having the right tools on hand, replacing office chair parts can be a smooth and cost-effective way to extend the life of your chair.
Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance helps extend the life of your office chair and keeps it functioning smoothly. Here are some simple tips to keep your chair in top condition:
- Rotate Cushions Regularly: For chairs with cushions, rotating them every few months helps distribute wear evenly, preventing sagging and prolonging their life.
- Protect from Sunlight and Heat: Direct sunlight and extreme temperatures can damage upholstery and plastic components. Place your chair away from windows or heat sources to protect it from fading and cracking.
- Use a Chair Mat: If you have carpeted flooring, consider using a chair mat to prevent the wheels from wearing down and to avoid friction that could damage both the chair and the floor.
- Air Out Fabric Upholstery: If your chair has fabric upholstery, it’s a good idea to air it out every few months to prevent odors from building up. Use a fabric-safe cleaner or deodorizer to refresh the material.
By adopting these tips, you'll not only maintain your chair’s condition but also enhance your overall seating experience. Regular upkeep ensures your chair supports you comfortably for years to come.

FAQs
1. What are the parts of a chair called?
The main parts of a chair include the base, seat pan, gas lift cylinder, armrests, backrest, casters (wheels), and lumbar support. These components work together to provide comfort, support, and adjustability for the user.
2. What is the central part of a chair?
The central part of a chair is typically the seat pan. It serves as the primary surface where the user sits and is connected to the base and backrest. The seat pan plays a crucial role in determining the chair’s overall comfort and ergonomics.
3. What makes up a chair?
A chair is made up of several key components, including the base, seat, backrest, armrests, gas lift cylinder, tilt mechanism, and casters. These parts can vary in design depending on the type of chair (e.g., office chair, gaming chair), but generally include these essential elements to provide comfort and functionality.
4. What is the thing that makes a chair go up and down?
The mechanism that allows a chair to go up and down is the gas lift cylinder. This hydraulic component uses gas pressure to enable smooth height adjustments, ensuring that the chair can accommodate users of different heights and desk setups. The gas lift is typically controlled by a lever beneath the seat.
5. How do I replace the gas lift cylinder in my office chair?
To replace the gas lift cylinder, first, remove the base and seat pan. Use a wrench to loosen the cylinder, then insert a new one and secure it back in place. Ensure the new cylinder is compatible with your chair model for smooth functionality.
If you need guidance on removing the base, check out our guide on how to remove the office chair base for detailed steps.
6. Can I replace the casters on my office chair myself?
Yes, you can easily replace the casters of your office chair. Simply pull out the old casters from the base and snap in the new ones, ensuring they match the size and type needed for your chair and floor surface (soft or hard).

7. Why does my office chair keep sinking?
Your office chair keeps sinking due to a faulty gas lift cylinder. This part loses its ability to hold the chair at a set height, requiring a replacement to restore functionality and adjustability. Replacing the gas lift will fix this issue, following this step-by-step guide to fix a sinking office chair, and prevent the chair from sinking unexpectedly.
8. Can I still use my office chair with a broken part?
If your office chair has a broken part, it may still be usable depending on the severity of the damage. Some components, like armrests or casters, can be easily replaced. However, for larger issues such as a broken gas lift or frame, it’s best to consult the manufacturer or retailer for replacement options, especially if the chair is still under warranty.
9. Is it normal for my office chair to wobble?
An office chair should not wobble. While some movement can occur due to its adjustable components, excessive wobbling could indicate improper assembly or a worn-out base. To check for wobble, place the chair on a flat surface and gently jiggle it. If the chair wobbles, it may need adjustments or replacement parts to restore stability.
10. What should I do if my office chair won't recline anymore?
If your office chair is stuck in a non-reclining position, the recline mechanism is likely faulty. This mechanism allows the backrest to tilt back, and if it’s malfunctioning, it will need to be replaced. Contact the manufacturer to find the correct replacement part, or seek professional help for repairs.
11. Why does my office chair hurt my back?
Back pain from your office chair can result from poor lumbar support, incorrect armrest height, or an improper ergonomic setup. Ensure your chair provides adequate lumbar support, and adjust the armrests to reduce strain on your neck and shoulders. Regular adjustments and choosing an ergonomic design can help alleviate back discomfort. Refer to the chair’s manual for optimal settings.
12. Why does my office chair smell?
A foul odor in your office chair may be due to worn-out seat padding or upholstery. Consider replacing the seat cushion or reupholstering the backrest. To prevent odors, choose chairs with mesh fabric, which promotes airflow and reduces sweating. Regular cleaning and ensuring good office ventilation can also help keep your chair smelling fresh.

Conclusion
Knowing the parts of a chair is essential for maintaining comfort, enhancing productivity, and extending the lifespan of your chair. Whether you're dealing with worn-out casters, adjusting the gas lift cylinder, or ensuring your lumbar support is in good condition, regular inspections and replacements can make a significant difference.
By understanding the different parts of a chair and how they function together, you can optimize your chair's performance and avoid unnecessary repairs. For those with a gaming chair, you can dive deeper into its parts and replacements in our guide on exploring different parts of a gaming chair.
Remember, a well-maintained chair promotes better posture, reduces discomfort, and ultimately supports your overall well-being.
Spread the word
.svg)