Edge AI vs. Cloud AI: Key Differences and Benefits for Your Business
Table of Contents
As the demand for artificial intelligence (AI) grows, the debate between Edge AI and Cloud AI has become increasingly important. Both technologies are reshaping industries and revolutionizing the way we process and analyze data. However, they approach AI differently: Edge AI performs computations locally on devices, while Cloud AI relies on remote servers for processing. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both is crucial in selecting the right technology for your business needs. This article dives deep into Edge AI vs. Cloud AI, their differences, benefits, and use cases, highlighting how each technology plays a role in today’s world.
1. What Is Edge AI?
Edge AI refers to the deployment of AI algorithms and models directly on edge devices such as sensors, cameras, wearables, and IoT devices. Unlike traditional AI systems that rely on sending data to the cloud for processing, Edge AI computing allows data to be processed locally, offering real-time decision-making capabilities. By processing data at the source, Edge AI reduces latency, enhances privacy, and ensures faster responses.
With Edge AI, businesses and individuals can process large datasets without relying on a constant internet connection, making it ideal for applications that require immediate action or in remote environments with limited connectivity. From smart devices to autonomous vehicles, Edge AI enables intelligent systems to perform tasks locally without waiting for cloud-based computations.
Edge AI Use Cases
- Autonomous Vehicles:
Edge AI is essential for autonomous vehicles, processing real-time sensor data such as cameras and LIDAR to make immediate decisions on navigation, obstacle detection, and collision avoidance.
- Healthcare:
Wearable health devices with Edge AI can monitor vital signs in real-time, detect abnormalities like arrhythmias, and send alerts to healthcare providers for immediate action.
- Manufacturing:
Edge AI can be used for predictive maintenance, where IoT sensors monitor equipment in real-time, identifying potential failures before they happen and optimizing production schedules.
.webp)
2. What Is Cloud AI?
In contrast, Cloud AI refers to the practice of processing and analyzing data remotely via cloud-based servers. It involves sending data from devices to the cloud for computation, where it is processed in data centers with high computational power and storage capacity. Cloud AI excels in scalability, offering extensive resources that are ideal for large-scale AI model training, data storage, and analytics.
Cloud AI works well for applications that require heavy computational tasks, such as training deep learning models or analyzing vast amounts of data. However, it introduces higher latency due to the need to transmit data to and from the cloud, which can be a drawback for real-time applications.
Cloud AI Use Cases
- AI Model Training:
Cloud AI is ideal for training deep learning models that require large datasets and immense computational power. It allows businesses to scale their operations without needing to invest in high-end hardware.
- Big Data Analytics:
Cloud AI is perfect for processing large volumes of data and running complex algorithms to uncover trends, insights, and predictions. This is especially useful in industries like finance, retail, and e-commerce.
- NLP and Deep Learning Models:
Cloud AI can run advanced models for natural language processing (NLP), machine translation, and other deep learning tasks that need significant processing power.
3. Key Differences Between Edge AI and Cloud AI
Feature | Edge AI | Cloud AI |
Data Processing Location | Processes data locally on edge devices (e.g., sensors, cameras, IoT devices) | Processes data in remote, centralized cloud servers |
Latency | Low latency, real-time processing | Higher latency due to data transfer between devices and the cloud |
Data Privacy | Enhanced privacy, as data stays local on the device | Lower privacy, as data is transmitted to and stored on cloud servers |
Bandwidth Usage | Requires minimal bandwidth since data is processed locally | High bandwidth usage as data needs to be transferred to and from the cloud |
Computational Power | Limited by device capabilities but suitable for real-time tasks | Provides higher computational power due to cloud-based resources |
Scalability | Limited scalability due to local processing constraints | Easily scalable with the vast resources of cloud infrastructure |
Cost | Lower operational costs, especially in the long term (no ongoing cloud fees) | Higher long-term costs, due to cloud usage fees, especially for large datasets |
Security | Increased security by keeping data on the device and reducing third-party exposure | Lower security, since data is transferred over the internet and stored off-site |
Flexibility | Works in environments with limited or no internet connectivity | Relies on stable internet connections for data processing |
Maintenance | Requires on-site maintenance and management | Maintenance and updates are handled by cloud service providers |
Use Cases | Ideal for real-time decision-making, IoT, autonomous vehicles, healthcare | Best for large-scale training, analytics, and long-term data storage |
3.1. When Should You Use Edge AI?
- Real-time applications where immediate decision-making is crucial, such as in healthcare, autonomous vehicles, and security.
- Remote or disconnected environments where consistent internet access is unavailable, like oil rigs, rural areas, or disaster zones.
- Privacy-sensitive applications, such as healthcare or finance, where data security is a top priority, and data must be processed locally to comply with regulations.
- To reinforce protection in these environments, organizations should also consider partnering with some of the top AI security vendors who specialize in localized AI system safeguards.
3.2. When Should You Use Cloud AI?
- Heavy computational tasks, such as model training, data analysis, and machine learning, which require more processing power than Edge AI can provide.
- Global-scale applications that need the flexibility of dynamically scaling computational resources, like big data analytics, business intelligence, and real-time customer insights.
- Collaboration and sharing of data and insights across teams, where centralization in the cloud is beneficial for updating models, sharing data, and integrating across multiple locations.
.webp)
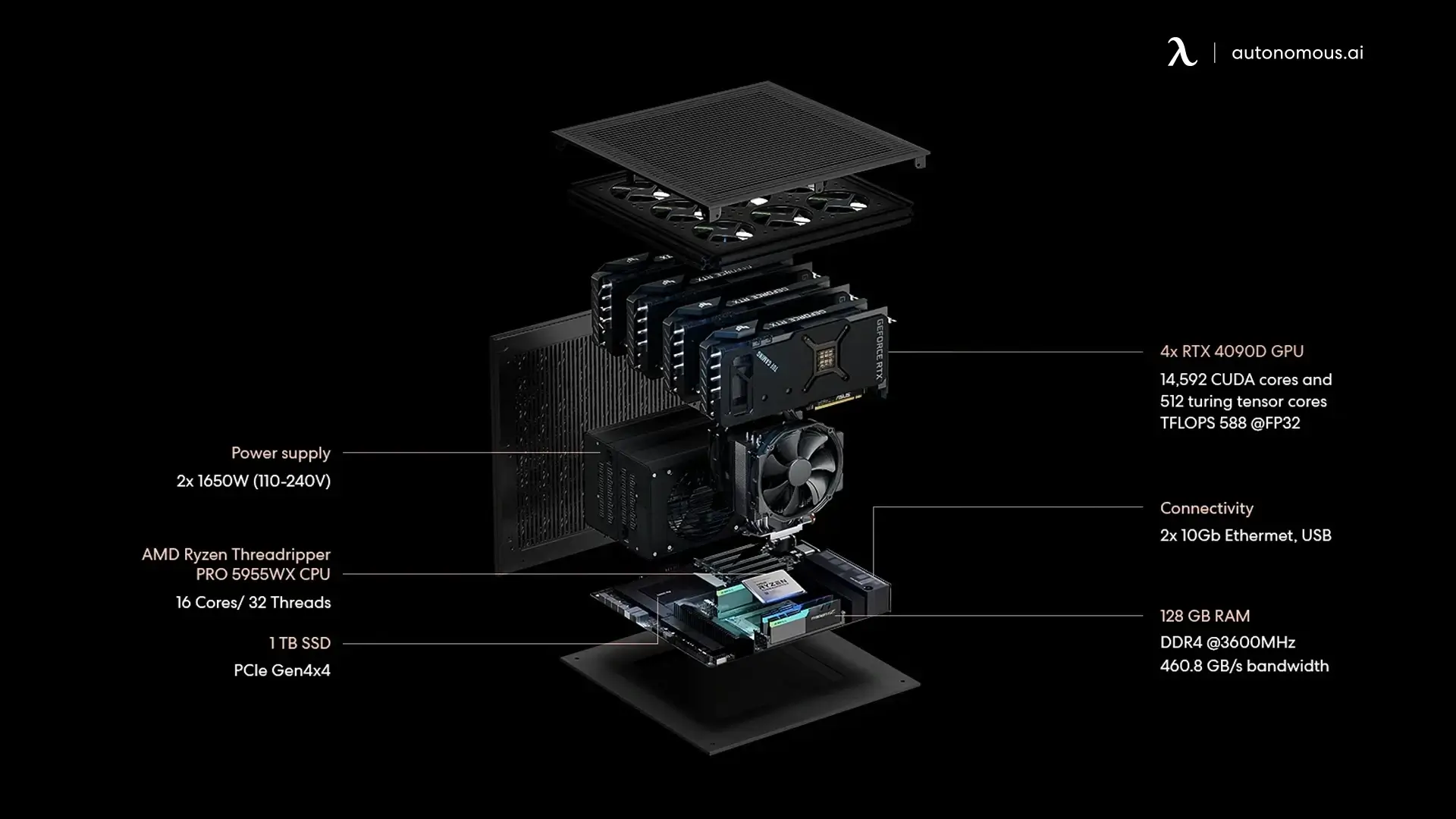
4. EdgeAI Computer: Revolutionizing AI with Local Processing
While Edge AI and Cloud AI have their respective strengths, the EdgeAI Computer bridges the gap by offering the power of local data processing with the performance of high-performance GPUs. Designed to deliver advanced AI computing, the EdgeAI Computer enables businesses to deploy and run AI models locally, without relying on cloud infrastructure. Here’s why you should consider the EdgeAI Computer for your business:
- Unmatched AI Performance: Powered by NVIDIA RTX 4090D GPUs, the EdgeAI Computer delivers over a petaflop of AI performance, ideal for demanding tasks like AI model training, data analysis, and real-time decision-making.
- Massive Scalability: With configurations ranging from 2 to 8 GPUs, the EdgeAI Computer can handle massive AI workloads, making it scalable for teams of all sizes.
- 100% Privacy: All AI workloads are processed locally, ensuring complete privacy and data security. No data is sent to the cloud, reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Cost-Effective: With no ongoing cloud costs, businesses can save significant amounts of money by choosing the EdgeAI Computer. It offers 96% savings compared to traditional cloud providers like Google Cloud.
5. FAQs
What is the main difference between Edge AI and Cloud AI?
Edge AI processes data locally on devices like sensors and cameras, offering low-latency, real-time decision-making. Cloud AI relies on centralized servers for data processing, introducing higher latency due to data transfer.
When should I use Edge AI instead of Cloud AI?
Edge AI is ideal for time-sensitive applications that require immediate action, such as autonomous vehicles, smart homes, and industrial IoT. It's also suitable for remote environments and privacy-sensitive tasks.
How does Edge AI help with privacy?
Edge AI keeps data processing local, reducing the need to transmit sensitive information over the internet. This ensures that data stays within the device, offering better privacy protection than cloud-based systems.
What industries benefit from Edge AI?
Industries like healthcare, manufacturing, automotive, and smart cities benefit from Edge AI. For example, healthcare devices like wearables can monitor vital signs and send alerts in real-time without relying on the cloud.
What are the benefits of using Cloud AI?
Cloud AI offers powerful computational capabilities and vast storage capacity, making it ideal for tasks such as training large-scale machine learning models and performing deep data analytics. It’s also flexible and scalable for enterprises with fluctuating needs.
Which is more cost-effective: Edge AI or Cloud AI?
Edge AI can be more cost-effective for businesses because it avoids recurring cloud service costs, especially for continuous, real-time data processing. Cloud AI may incur ongoing costs based on usage and data storage but offers scalable computing resources.
Can Edge AI and Cloud AI work together?
Yes, a hybrid approach can be beneficial. Edge AI handles real-time tasks locally, while Cloud AI can be used for tasks like model training, large-scale data analysis, and integrating AI models across multiple devices.
Does Edge AI require an internet connection?
No, Edge AI can operate independently of an internet connection, as it processes data locally. This makes it suitable for remote or disconnected environments.
What is the future of Edge AI and Cloud AI?
Both Edge AI and Cloud AI will continue to evolve. Edge AI will become more powerful and integrated into real-time decision-making systems, while Cloud AI will still play a crucial role in handling large-scale data processing, model training, and analytics, with increasing integration of 5G and AI technologies.
How does the EdgeAI System fit into this?
The EdgeAI System is a powerful on-premises solution that brings the best of both worlds by offering local AI processing with scalability and high-performance capabilities. It allows businesses to run complex AI models and make real-time decisions without relying on cloud infrastructure.

6. Conclusion
Both Edge AI and Cloud AI are critical technologies in the AI ecosystem, each with its unique advantages. Edge AI excels in real-time applications, privacy, and cost-effectiveness, while Cloud AI shines in scalability and heavy computational tasks. The EdgeAI Computer offers the best of both worlds by providing local data processing with the performance of high-end GPUs, making it ideal for businesses that need fast, efficient, and secure AI computing.
For a better understanding of AI PC meaning, the differences in how these systems function are important. Additionally, exploring the capabilities of an AI PC assistant can significantly improve your productivity by managing tasks more efficiently. To dive deeper into Edge AI meaning, it’s essential to understand how this technology is revolutionizing industries by processing data locally.
Spread the word
.svg)

.webp)
.webp)