AI Assistants: How They Work & Best Tools (2026 Guide)
Table of Contents
AI assistants have moved well past setting timers and answering trivia. Today's tools draft emails, manage calendars, write code, and run multi-step workflows with minimal input. But the category has gotten noisy — dozens of products claim to do everything, making it harder to figure out what actually fits your workflow.
This guide breaks down how AI assistants work under the hood, the main types available now, and which tools deliver real value depending on what you need them to do.
What Is an AI Assistant?
An AI assistant is software that uses artificial intelligence to understand natural language and complete tasks through conversation. You type or speak a request, and it responds with useful output — an answer, a draft, a scheduled meeting, a summary of a 40-page document.
That definition covers a wide range. A personal AI assistant like Siri handles voice commands on your phone. A ChatGPT AI assistant session helps you brainstorm marketing copy or debug code. An office AI assistant built into Microsoft 365 pulls action items from meeting transcripts and drops them into your task list. They all qualify, but they solve very different problems.
The technology driving them has shifted significantly. Early AI assistants ran on rigid scripts — if your phrasing didn't match their rules, they failed. Modern ones are built on large language models trained across massive datasets, which means they interpret meaning and context rather than matching keywords. They understand that "move my 3 pm to Thursday" and "reschedule this afternoon's call to later in the week" are the same request.
AI Assistant vs. Chatbot
Chatbots follow pre-built decision trees. They handle FAQ pages and order tracking well enough, but the moment a conversation goes off-script, they stall. AI assistants work differently. They hold context across an entire conversation, interpret ambiguity instead of choking on it, and generate original responses rather than pulling from a fixed library. If a chatbot is a vending machine — press the right button, get a set output — an AI assistant is closer to a colleague who listens, thinks, and responds based on what you actually meant.
AI Assistant vs. AI agent
This distinction matters more in 2026 than it did a year ago. An AI assistant waits for your input — you ask, it delivers. An AI agent pursues a goal autonomously. You tell it "keep my inbox under 20 unread emails," and it triages, drafts replies, and archives on its own. Most AI assistant platforms are adding agentic features, blurring the line. But for now, the core difference is initiative: assistants react, agents act. But for now, the core difference is initiative: assistants react, AI agents vs. AI assistants is worth understanding before choosing your next tool.
For anyone evaluating an AI assistant for business use or personal productivity, understanding these distinctions prevents buying a chatbot when you need an assistant or expecting autonomous execution from a tool that still needs you in the loop.

How Do AI Assistants Work?
Every AI assistant follows the same basic loop, whether it's a free AI assistant answering a quick question or an enterprise tool managing workflows across departments. The process has five stages, and understanding them makes it easier to judge where a tool is strong and where it's likely to fall short.
- Input:
You type a prompt, speak a command, or share a file. For voice, speech recognition translates sound into text — preserving intent across accents, noise, and half-finished sentences.
- Understanding:
Natural language processing parses the structure of your request, not just the keywords. "Send the Q3 deck to Sarah and ask if Tuesday works" requires the assistant to separate two actions, identify the right contact, find the file, and infer which Tuesday you mean.
- Retrieval:
LLMs carry broad knowledge, but it has a cutoff. Many AI assistant platforms layer in retrieval-augmented generation, pulling real-time data from your calendar, email, CRM, or the web before responding. This is the difference between "I don't have that information" and an actual answer.
- Response generation:
Output is constructed word by word from your context, retrieved data, and trained patterns — not selected from a template. The best AI assistants for work ground responses in your specific situation rather than producing generic output.
- Learning:
Most assistants don't retrain from your conversations in real time. They refine context within sessions and store preferences across them. A Gemini AI assistant remembers your response length settings. ChatGPT carries custom instructions between chats. This layer is early, but it's where useful becomes indispensable.
The quality of any AI assistant depends on how well these stages connect. Strong retrieval with weak generation buries good information in a bad response. A powerful model with no real-time data gives you confident answers built on stale facts. The tools worth using get the full chain right.
Types of AI Assistants
The category has grown broad enough that calling something "an AI assistant" doesn't tell you much on its own. What matters is what it's designed to do and where it operates. Five types cover most of what's available today.
- Virtual Personal Assistants:
Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant. These are voice-first tools built into phones, speakers, and smart home devices. They handle quick commands well — setting timers, playing music, checking the weather, and controlling lights.
Where they fall short is depth. Ask a personal AI assistant like Alexa to summarize a report or draft an email, and you'll hit a ceiling fast. Their strength is convenience and device integration, not complex reasoning.
- Generative AI Assistants
This is where ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini live. Built on large language models, they handle open-ended work: writing, analysis, coding, research, and brainstorming. These tools are general-purpose by design, which makes them flexible but also means they're only as useful as the prompts and context you give them.
For workflows centered on content and documentation, there's significant overlap with dedicated AI writing tools that trade breadth for deeper writing-specific features.
- Enterprise Workplace Assistants:
Microsoft Copilot is the clearest example — an office AI assistant embedded across Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook, and Teams. It pulls data from your organization's files and communications to generate responses grounded in internal context.
Other players like Moveworks and Guru focus on IT support and internal knowledge retrieval. An AI assistant for business in this category lives inside the tools your team already uses, which removes the friction of switching between apps but often locks you into a specific ecosystem.
- Task-Specific Assistants:
Not every problem needs a general-purpose model. GitHub Copilot focuses entirely on code generation and autocompletion. Motion and Reclaim optimize scheduling by analyzing calendars and priorities. Jasper and Writer target content production with built-in brand voice controls. These tools trade breadth for precision — they do one thing and do it well.
- Agentic AI Assistants:
The newest and fastest-evolving category. Tools like Lindy let you build custom AI agents that execute multi-step workflows autonomously — triaging emails, updating CRMs, scheduling follow-ups — without waiting for a prompt at each step.
The best AI assistants in this space combine no-code builders with deep integrations, letting non-technical users automate complex sequences. As these systems mature, they’re also being explored in adjacent areas such as wellbeing and workload management, intersecting with broader discussions around AI for mental health in the workplace.
The lines between these types are blurring. Generative assistants are adding agentic features. Enterprise tools are integrating general-purpose models. Personal assistants are getting smarter. But knowing which type fits your actual need — quick commands, deep knowledge work, team-wide automation — is still the most practical filter before evaluating any specific product.

Best AI Assistants in 2026
Choosing the right AI assistant depends less on which one is "best" and more on what you actually need it to do. A tool built for deep research won't help you manage your calendar, and a scheduling assistant won't write your quarterly report.
The 7 tools below were selected based on practical capability, integration depth, and where each one fits in a real workflow — not marketing claims. Each includes a clear limitation, because no tool does everything well.
- Side-by-Side Comparison:
Tool | Best For | Limitation | Price |
ChatGPT | General-purpose writing, coding, and research | Weak session-to-session memory | Free / $20/mo |
Claude | Long-document analysis, complex writing | Limited third-party integrations | Free / $20/mo |
Gemini | Google Workspace–embedded workflows | Underperforms outside the Google ecosystem | Free / $19.99/mo |
Microsoft Copilot | Enterprise Office 365 productivity | Expensive; locked to the Microsoft stack | $30/user/mo |
Perplexity | Sourced research and fact-checking | No content generation or integrations | Free / $20/mo |
Granola | Meeting notes and conversation capture | Meetings only, nothing else | Free / $18/mo |
Reclaim | AI-driven calendar and time management | No mobile app; scheduling only | Free / $10/user/mo |
1. ChatGPT
Best for: Generalists who need one tool across writing, coding, research, and light automation.
ChatGPT is the default starting point for most people exploring AI assistants, and for a practical reason — it handles the widest range of tasks without requiring setup or specialization. You can draft a blog post, debug a script, analyze a spreadsheet, brainstorm product names, and summarize a research paper in the same session. The model flexibility helps too: GPT-4o covers everyday work well, while o3 handles tasks that need deeper reasoning.
Where ChatGPT earns its place is in the ecosystem around it. Custom GPTs let you build reusable mini-assistants tuned to specific tasks — a weekly report formatter, a tone-of-voice checker, a competitor research bot. Plugin and integration support extends into Zapier, Google Docs, Slack, and more, which makes it functional beyond the chat window. The desktop app adds a coding canvas and collaborative writing tools that push it closer to a working environment than a simple Q&A interface.
The limitation is continuity. ChatGPT struggles to retain context between sessions without repeated prompting. It doesn't remember your preferred frameworks, past decisions, or project-specific details unless you manually set custom instructions — and even those have depth limits. For one-off tasks, it's excellent. For ongoing work that builds on itself week over week, you'll feel the gaps.
Price: Free tier available. Plus at $20/month. Pro at $200/month.

2. Claude
Best for: Knowledge workers handling long documents, complex writing, and analysis-heavy tasks.
Claude AI takes a different approach than most generative AI assistants. Where other tools optimize for speed and breadth, Claude leans into depth — long-context reasoning, nuanced writing, and extended analysis that holds together across complex inputs.
That strength makes it particularly effective as an AI assistant for work that involves synthesis. Comparing vendor proposals, reviewing dense documentation, drafting detailed briefs from scattered source material — these are tasks where Claude consistently outperforms tools that prioritize quick, surface-level output. Its writing style is more structured and natural, which matters when the output is delivered directly to clients, investors, or internal teams rather than used as a rough draft.
Claude also includes built-in file creation and a code execution environment. This allows it to generate polished documents, analyze uploaded data, and produce working artifacts — not just text responses. The Projects feature enables persistent context and custom instructions, helping maintain continuity across longer workflows and partially addressing the session-to-session memory limitations common in many AI assistants.
The main limitation is ecosystem depth. Claude lacks the plugin marketplace and third-party integrations available in some competing AI assistants. It functions best as a focused workspace rather than a central hub across a broader tool stack. For workflows that rely on automations, triggers, or multi-app connectivity, Claude may feel more contained.
Price: Free tier available. Pro at $20/month. Team at $30/user/month.
3. Gemini
Best for: Teams and individuals already invested in Google Workspace who want AI embedded in their daily tools.
Gemini's core advantage isn't the model itself — it's where the model lives. As Google's AI assistant, Gemini is embedded directly into Gmail, Docs, Sheets, Slides, Meet, and Calendar. That integration means it operates inside the tools rather than alongside them. You're not copying text between apps. You're drafting a reply inside your inbox, cleaning data inside your spreadsheet, or generating a presentation outline inside Slides — all without leaving the tab you're already in.
For teams already running on Google Workspace, this creates a level of workflow friction reduction that standalone AI assistants can't match. Gemini summarizes email threads in Gmail, suggests edits in Docs with full document context, and pulls meeting action items from Meet transcripts directly into Tasks. The Gemini AI assistant also supports multimodal input — upload documents, images, or audio and get responses grounded in the full file, not just extracted text.
Deep Think mode adds a step-change for heavier tasks, breaking complex problems into structured reasoning steps. It's useful for financial reviews, report analysis, and anything that benefits from methodical rather than rapid output. On mobile, Gemini Nano handles lightweight requests on-device with lower latency and no cloud dependency.
The limitation is the walled garden. Gemini thrives inside Google's ecosystem and underperforms outside it. If your team splits across Microsoft, Notion, Slack, or other non-Google tools, the integration advantage shrinks considerably. You're getting a powerful personal AI assistant for Google — not a universal one.
Price: Free tier available. Google One AI Premium at $19.99/month.

4. Microsoft Copilot
Best for: Organizations already using Microsoft 365 that want AI integrated at the enterprise level without onboarding a separate platform
Microsoft Copilot is the clearest example of an office AI assistant designed for enterprise-scale adoption. It's built into Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook, and Teams — the tools that already dominate most corporate environments. That positioning means Copilot doesn't need to convince organizations to adopt a new platform. It just shows up inside the one they already pay for.
Copilot delivers the most value in everyday knowledge work. In Word, it drafts documents using context from SharePoint and internal files. In Excel, it creates formulas, summaries, and visualizations from plain-language prompts. In Teams, it generates meeting recaps with action items assigned to specific participants. In Outlook, it summarizes long email threads and suggests responses aligned with the conversation’s tone. Individually, these features save minutes; across teams and weeks, the time savings compound into a clear ROI.
For IT and operations teams evaluating an AI assistant for business deployment, Copilot aligns well with enterprise requirements. It operates within Microsoft 365’s existing security framework, including data governance, role-based access controls, and audit logging. Copilot also respects organizational permissions, ensuring employees only see content they are already authorized to access.
The primary limitations are cost and ecosystem dependency. At $30 per user per month on top of Microsoft 365 licensing, Copilot is among the most expensive AI assistants available. Its effectiveness also drops sharply outside the Microsoft ecosystem. If workflows rely heavily on non-Microsoft tools, Copilot becomes powerful within part of the stack and largely absent elsewhere.
Price: $30/user/month (requires Microsoft 365 subscription).
5. Perplexity
Best for: Researchers, analysts, and anyone whose work depends on accurate, sourced information rather than generated text.
Perplexity occupies a different space than the other tools on this list. It's not built for content generation or workflow automation — it's built for research. Ask a question, and Perplexity returns a structured answer with inline citations linked to original sources. You can see exactly where each claim comes from, verify it, and follow the trail deeper. That transparency makes it more trustworthy for factual work than generative AI assistants that present information confidently without showing their evidence.
The experience feels closer to having a research analyst on call than a chatbot. Perplexity pulls from live web data by default, so the answers reflect current information rather than a static training cutoff. For tasks like competitive analysis, market research, fact-checking statistics before a presentation, or exploring an unfamiliar topic before committing to a direction — it consistently delivers cleaner, more reliable starting points than asking a general-purpose model the same question.
Pro features expand into deeper territory with support for file uploads, longer multi-step research sessions, and model selection across multiple providers. The interface stays minimal throughout, which keeps the focus on the output rather than the tool itself.
The limitation is scope. Perplexity doesn't write long-form content well, can't execute code, won't manage your calendar, and has no meaningful integration layer with other work tools. It does one thing — answer questions with sourced evidence — and stops there. If you need the best AI assistant that handles end-to-end workflows, this isn't it. If you need answers you can trust, it's hard to beat.
Price: Free tier available. Pro at $20/month.
6. Granola
Best for: Professionals in back-to-back meetings who need reliable, structured notes without disrupting the conversation.
Granola solves a narrow problem exceptionally well: meeting notes. It runs quietly on your device, transcribing audio from Zoom, Google Meet, Teams, Slack, or WebEx without injecting a bot into the call. There’s no “AI assistant is joining this meeting” notification and no change in participant behavior. Granola listens through your computer’s audio and works entirely in the background.
What separates Granola from standard transcription tools is the collaborative layer. You can type your own shorthand notes during the meeting — fragments, keywords, half-thoughts — and Granola merges them with the full transcript to produce structured, readable output the moment the call ends. The AI understands meeting context, distinguishing between sales calls, interviews, and project kickoffs, and formats outputs accordingly. Action items, decisions, and key takeaways surface automatically without manual tagging.
Granola 2.0 expanded into team functionality with shared folders, cross-meeting search, and the ability to ask questions across weeks of conversations. For managers and team leads running back-to-back calls, that cumulative knowledge layer turns meeting notes from disposable artifacts into a searchable AI assistant for work — one that actually remembers what was discussed three Tuesdays ago.
The limitation is specialization. Granola is built for meetings and nothing else. It does not draft emails, analyze datasets, or manage tasks. If your productivity bottlenecks live outside of calls, Granola won’t solve them. But for teams drowning in conversations and losing decisions to poor documentation, it fills a gap that general-purpose AI assistants often overlook.
Price: Free tier available. Pro at $18/month. Business pricing for teams.
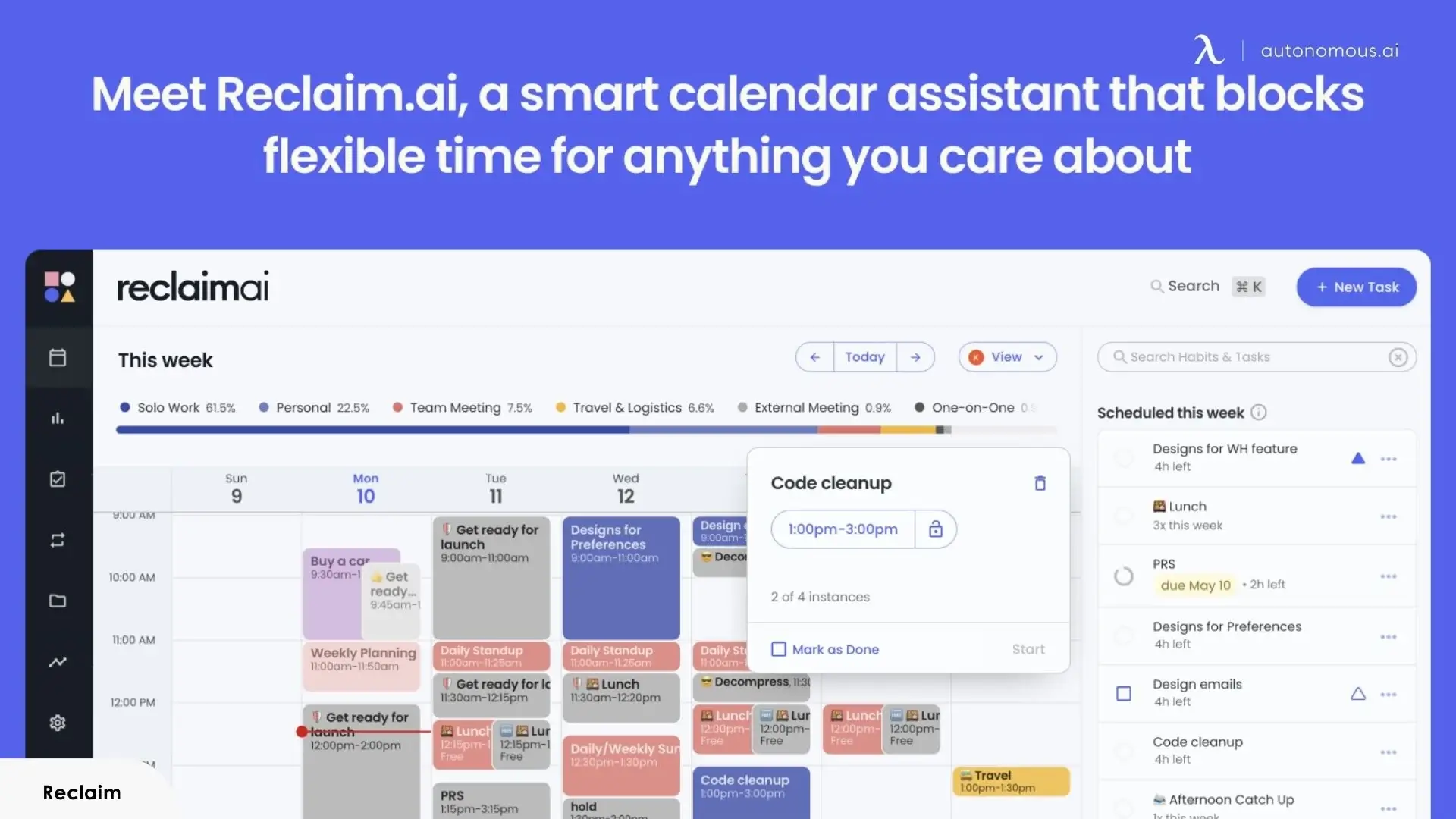
7. Reclaim
Best for: Busy professionals and team leads who need AI-driven calendar management to protect focus time and reduce scheduling overhead.
Reclaim approaches productivity from a different angle than the other tools here. Instead of helping you create content or answer questions, it manages the resource most AI assistants ignore entirely — your time. Connect your Google Calendar or Outlook, set your priorities, and Reclaim's AI builds your week around them. Focus time, recurring habits, task deadlines, breaks, and meetings all get scheduled automatically based on what actually matters, not just what showed up in your inbox first.
The intelligence is in the flexibility. Reclaim doesn't just block time statically — it holds slots as tentative until your calendar fills up, then locks them in to protect your priorities. If a conflict appears, it reshuffles. If a task takes longer than expected, it reschedules the rest. The result is a calendar that adapts throughout the week without you manually dragging blocks around every morning. For anyone who has tried time-blocking and abandoned it because maintenance felt like a second job, that automation is the difference.
Team features extend the same logic across groups. Smart Meetings finds optimal times across all attendees' schedules. Managers get workforce analytics showing how time splits across deep work, meetings, and collaboration — data that's useful for capacity planning and burnout prevention. The Dropbox acquisition in 2024 signals deeper integration ahead, though the current product already connects with Asana, Todoist, ClickUp, Jira, Linear, and Slack.
The limitation is boundaries. Reclaim is an AI assistant free to start, but it's purely a scheduling layer. It doesn't generate content, answer questions, or interact conversationally. There's no mobile app yet, which is a notable gap for a productivity tool in 2026. And its value scales directly with how meeting-heavy and calendar-driven your work is — if your days aren't structured around time blocks, the core benefit won't land.
Price: Free tier available. Starter at $10/user/month. Business at $18/user/month.
No single tool on this list replaces the others. The strongest setup for most people is a general-purpose assistant for thinking work — writing, analysis, research — paired with one or two specialized tools that handle the tasks a generalist can't. A ChatGPT or Claude session for strategy and content, Reclaim for protecting your calendar, and Granola for capturing what happens in meetings. The right combination depends on where your time currently leaks, not on which tool has the longest feature list.
How to Choose the Right AI Assistant For Work
The tools above cover different categories for a reason — no single AI assistant handles every workflow well. Choosing the right one starts with identifying what you actually need automated, not which product has the most features or the highest profile.
- Start with the task, not the tool:
If your days revolve around writing, analysis, and research, a generative assistant like ChatGPT, Claude, or Perplexity fits. If your bottleneck is scheduling and calendar chaos, Reclaim solves that directly. If you're losing decisions and action items across back-to-back calls, Granola targets that specific gap. Matching the tool to the problem sounds obvious, but most people do it backward — they pick a popular tool and then look for ways to use it.
- Check where you already work:
The best AI assistants are useless if it doesn't connect to your existing tools. Google Workspace teams get more from Gemini than from Copilot. Microsoft 365 organizations get the reverse.
If your stack is fragmented across multiple platforms, a standalone tool like ChatGPT or Claude gives you flexibility without ecosystem lock-in. For developers, dedicated AI tools for coding often integrate better with IDEs than general-purpose assistants.
- Be realistic about what free gets you:
Most AI assistants offer a free tier, and for light individual use, it's often enough. But free versions typically cap usage, limit model access, and restrict features like file uploads or team collaboration. If you're evaluating an AI assistant for business deployment across a team, test the paid tier — the free experience won't reflect what your team actually needs at scale.
- Don't over-consolidate:
The instinct to find one tool that does everything usually leads to mediocre results across the board. A focused pairing — one generalist for knowledge work, one specialist for protecting your deep work time — consistently outperforms a single tool stretched beyond its strengths. Desktop-level AI PC assistants can handle system-wide tasks that browser-based tools can't reach.

FAQs
What is an AI assistant?
An AI assistant is software that uses artificial intelligence to understand natural language and complete tasks through conversation. It can answer questions, generate content, summarize documents, schedule meetings, or manage workflows depending on its design.
What’s the best AI assistant to use?
The best AI assistant for work depends on the task you need automated. General-purpose AI assistants like ChatGPT or Claude work well for writing, analysis, and research, while task-specific assistants handle scheduling, meetings, or enterprise workflows more effectively.
Is ChatGPT an AI assistant?
Yes. ChatGPT is an AI assistant designed to understand natural language and help with tasks like writing, coding, research, analysis, and problem-solving through conversation. Unlike simple chatbots, it can reason across context, generate original output, and support multi-step work rather than just answering predefined questions.
What’s the difference between ChatGPT and Copilot for work?
ChatGPT is a general-purpose AI assistant designed for flexible writing, coding, and research across many tools. Microsoft Copilot is an enterprise AI assistant embedded directly into Microsoft 365, optimized for internal documents, emails, and meetings within that ecosystem.
Are AI assistants safe to use at work?
AI assistants can be safe for work when they follow enterprise security standards and data governance controls. Business-focused AI assistants typically respect permission boundaries and offer audit logs and access controls.
Do AI assistants see my files and emails?
AI assistants only access files and emails if you explicitly connect those systems. Enterprise AI assistants inherit existing permissions, meaning they can only surface content users are already authorized to view.
Are free AI assistants good enough?
Free AI assistants are suitable for light, individual use or experimentation. Paid plans usually provide better models, higher usage limits, file uploads, and collaboration features needed for consistent professional work.
Do I need more than one AI assistant?
Many professionals use more than one AI assistant to cover different workflows. A general-purpose assistant handles thinking and content work, while specialized tools manage calendars, meetings, or research more reliably than a single all-in-one solution.
What’s the difference between an AI assistant and an AI agent?
An AI assistant responds to prompts, while an AI agent acts autonomously toward a goal. Agents can execute multi-step workflows without constant input, whereas assistants still require you to stay in the loop.

Conclusion
AI assistants aren't a single category anymore. They range from general-purpose thinking partners to specialized tools that manage your calendar, capture your meetings, or source your research. The technology underneath — large language models, natural language processing, retrieval systems — has matured enough that the real question isn't whether these tools work. It's the combination that fits the way you actually operate, whether you need best AI tools for Marketing campaigns or AI image generation tools for creative workflows.
Start with the workflow that costs you the most time. Test one tool there. Once it sticks, layer in a second where the next bottleneck lives. That incremental approach — building a focused stack of best productivity apps that each solve a specific problem — delivers more than any all-in-one promise.
Spread the word
.svg)

.webp)
.webp)