.webp)
Office Humidity Levels: What’s Acceptable and What’s Ideal?
Table of Contents
- 1. What Is Office Humidity?
- 2. Normal and Ideal Office Humidity Levels
- 3. Acceptable Humidity Levels in Office Buildings
- 4. Common Causes of High Humidity in the Office
- 5. Low Humidity in the Office: Why It Happens
- 6. How Office Humidity Affects Daily Work
- 7. How to Reduce Humidity in an Office
- 8. Bringing Awareness Closer to the Desk
- 9. FAQs
- 10. Conclusion
Office humidity plays a larger role in daily comfort than many people realize. When humidity levels drift too high or too low, air can begin to feel dry, heavy, or uncomfortable, even if temperature seems fine. Because office work often involves long hours indoors, maintaining balanced humidity helps support comfort, focus, and overall wellbeing throughout the workday.
1. What Is Office Humidity?
Office humidity refers to the amount of moisture in the air inside office buildings, typically measured as relative humidity (RH). Relative humidity compares the moisture currently in the air to the maximum amount the air can hold at a given temperature.
Humidity changes are often gradual. Air may feel comfortable in the morning and become noticeably dry or heavy by the afternoon. Normal office humidity also varies with weather, occupancy, ventilation, and how different spaces are used. Because humidity is one part of the broader indoor environment, it’s closely connected to overall office air quality and how comfortable a workspace feels throughout the day.
2. Normal and Ideal Office Humidity Levels
Based on workplace guidance and building research, office humidity is generally discussed in ranges, not exact targets.
- Ideal office humidity: 40%–60% RH
- Common “sweet spot” for comfort and performance: 40%–50% RH
- Normal or acceptable office humidity: 30%–60% RH
The distinction matters. Conditions may fall within acceptable limits while still feeling uncomfortable. The ideal range is narrower and more closely associated with sustained comfort, reduced fatigue, and better concentration over long workdays.
.webp)
3. Acceptable Humidity Levels in Office Buildings
Acceptable humidity levels in office buildings are typically defined to prevent extremes rather than guarantee perfect comfort.
Most office humidity standards reference:
- 20%–60% RH as a broad operating range (often cited in occupational guidance)
- 30%–60% RH as a more practical comfort-focused range
- 40%–60% RH as the preferred zone for comfort, wellbeing, and reduced environmental risk
However, meeting office humidity standards does not mean every space will feel the same. Humidity can vary significantly depending on office building types, layout decisions, and how rooms are used throughout the day.
For example, desks placed near exterior walls or windows — such as a desk in front of a window — may experience different humidity conditions than interior workstations.
Flexible layouts also play a role. Some private office coworking spaces may experience different humidity patterns compared to dense cubicle layouts or open space office designs.
Even architectural choices such as an open ceiling concept or how teams arrange office furniture can influence airflow and moisture distribution. This is why offices can remain within acceptable humidity ranges overall while still experiencing uneven comfort from room to room or desk to desk.

4. Common Causes of High Humidity in the Office
High humidity in office environments occurs when moisture builds up faster than it can be removed. This often happens gradually and may not be noticeable until discomfort sets in.
Signs of High Humidity in the Office (Above 60%)
- Air feeling heavy or clammy
- Condensation forming on windows or surfaces
- Musty or damp odors in certain areas
Common Causes
- Insufficient ventilation or poor air circulation
- HVAC systems not balanced for actual occupancy
- Humid outdoor conditions during warmer seasons
- Enclosed spaces such as meeting or conference rooms
- Moisture from cleaning activities, kitchens, or nearby restrooms
When relative humidity rises above 60%, air often begins to feel heavier as the day goes on, especially in high-use or enclosed spaces such as an office boardroom, a modern office break room, or flex office room where occupancy and airflow change throughout the day.
5. Low Humidity in the Office: Why It Happens
Low humidity in office spaces is most common during colder months or in buildings that rely heavily on climate control.
Signs of Low Humidity in the Office (Below 30%)
- Dry or uncomfortable air during long workdays
- Static shocks from office equipment
- General dryness that becomes more noticeable over time
Typical Causes
- Heated air during winter months
- Over-conditioned HVAC systems
- Sealed buildings with limited moisture exchange
When humidity drops below 30%, dryness tends to build gradually rather than appearing all at once, which makes low humidity easy to overlook until discomfort becomes persistent.
6. How Office Humidity Affects Daily Work
Office humidity influences how air feels, how alert people remain, and how draining the workday becomes.
Balanced humidity supports:
- Sustained comfort
- Better concentration
- Fewer distractions from environmental discomfort
When humidity moves outside the ideal range, tasks may feel more effortful, meetings more tiring, and spaces less consistent across the same office.
.webp)
7. How to Reduce Humidity in an Office
Managing office humidity usually involves improving balance rather than relying on a single solution.
Common approaches include:
- Maintaining HVAC systems so moisture is properly regulated
- Improving ventilation to support moisture exchange
- Using humidifiers in dry conditions (kept below ~50%)
- Using dehumidifiers in damp areas where needed
Humidity control works best when coordinated with temperature and ventilation rather than treated as an isolated fix.

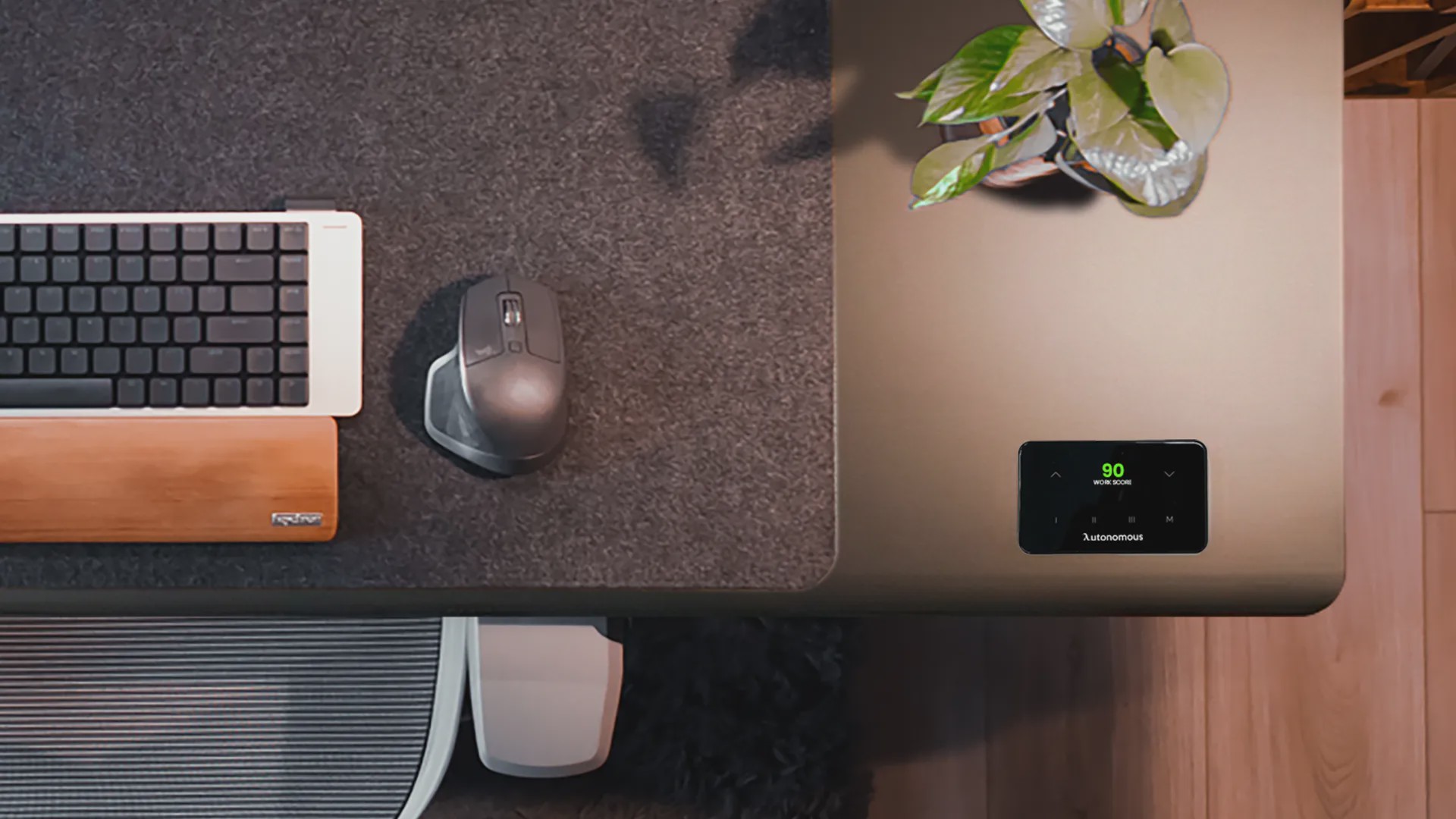
8. Bringing Awareness Closer to the Desk
Humidity can vary widely across a single office floor, and building-level systems don’t always reflect what individuals experience at their desks. Because most work happens at the workstation, this is often where humidity-related discomfort is noticed first.
This is where Autonomous Desk 5 AI fits naturally into the broader conversation. By bringing environmental awareness closer to the desk, workstation-level insight helps connect humidity conditions with everyday work experience, complementing existing HVAC and building systems rather than replacing them.
9. FAQs
What is the ideal humidity level for an office?
The ideal office humidity level is generally 40%–60% relative humidity, with many experts favoring 40%–50% for optimal comfort.
What is considered high humidity in an office?
Humidity levels above 60% RH are typically considered high and may lead to discomfort or damp conditions.
Is low humidity bad in an office?
Yes. Humidity below 30% RH can make air feel dry and uncomfortable, especially during winter months.
What is the OSHA recommended humidity level?
Occupational guidance often references a humidity range of 20%–60% RH, though comfort-focused recommendations usually narrow this to 30%–60% RH.
10. Conclusion
Office humidity is a subtle but influential part of the indoor work environment. Whether levels are too high or too low, imbalance tends to develop gradually and vary across spaces. By understanding ideal ranges, common causes, and how humidity changes throughout the day, offices can move beyond assumptions and create a productive work environment that better supports comfort, focus, and sustained work.
.svg)